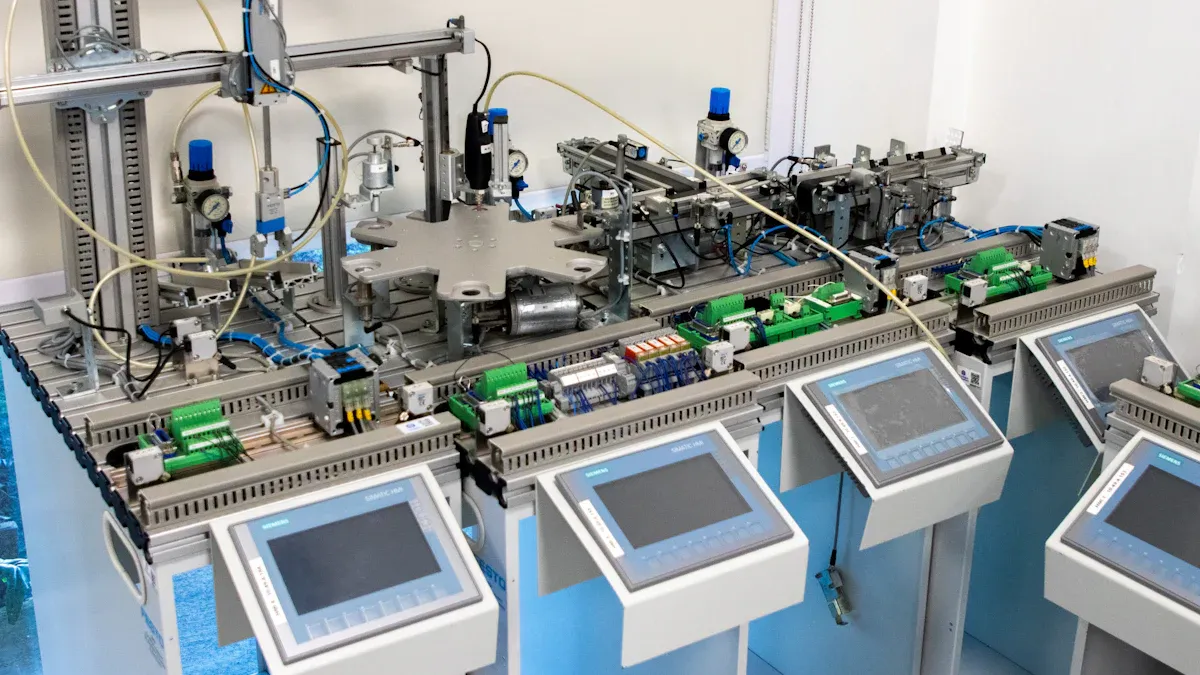

A printed circuit board (PCB) is the foundation of electronics, connecting various components to function together. When components such as resistors and chips are integrated into a PCB, it transforms into a PCBA, or printed circuit board assembly. Understanding the pcba manufacturing meaning is crucial, as a PCB serves as the skeleton while a PCBA acts as the brain. Recognizing this distinction is essential, especially with emerging trends like 5G and the demand for smaller devices, which require enhanced PCBs and more efficient PCBA methods. These advancements lead to devices that are better, smaller, and smarter.
Key Takeaways
A PCB is the foundation of electronics. It holds parts together.
A PCBA is a PCB with parts added. It can now work.
Checking quality is important for both PCB and PCBA. This ensures they are safe and reliable.
Machines help make PCBAs faster and with fewer mistakes. This improves the products.
Picking PCB or PCBA depends on your project, money, and needs.
PCB vs PCBA: Definitions and Components
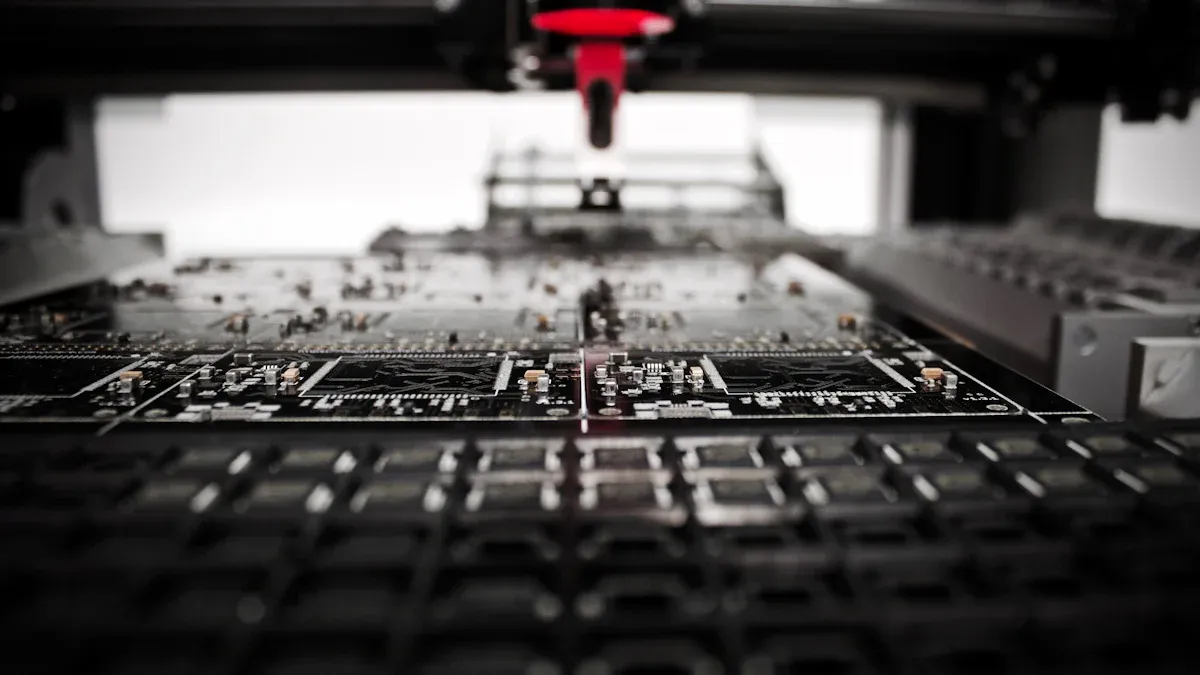
What is a PCB?
A printed circuit board (PCB) is the base of most electronics. It is a flat board made of insulating material, like fiberglass. Thin copper lines, called traces, are added to connect parts. These traces let electronic parts work together. PCBs give both support and electrical connections, making them very important in electronics.
Here are some main features of PCBs:
They have layers of copper and insulating material.
Copper traces carry electrical signals between parts.
Making PCBs involves steps like etching, laminating, and drilling.
PCBs are key in electronics. They hold parts in place and connect them so devices can work.
What is a PCBA?
When a PCB has all its parts added, it becomes a printed circuit board assembly (PCBA). This means parts like resistors and chips are attached to the PCB. The finished PCBA can perform tasks in an electronic device.
Making a PCBA includes these steps:
1. Building the PCB using design plans.
2. Getting the right parts for the design.
3. Adding parts using methods like SMT or soldering.
4. Checking and testing to ensure it works properly.
A PCBA is like the brain of a device. It handles signals, calculations, and controls based on its design.
Definition | |
|---|---|
PCB | A flat board with copper pathways that connect parts. |
PCBA | A PCB with all parts added, making it work. |
Key components of a PCB
PCBs have important parts that help them work well. Each part has a job to make sure the PCB does its job. Here’s a list of the main parts:
Circuit Board Layers: Layers of copper and insulating material, often FR-4.
Inner Layer Circuitry Creation: Circuitry is printed on inner layers with special material.
Oxide and Lamination: Oxides strengthen connectors, and layers are fused with heat.
Drilling: Holes are drilled to connect layers electrically.
Electroless Copper Deposition: Prepares outer layers to carry electricity.
Electroplating, Stripping, and Etching: Adds copper and forms the final traces.
Solder Mask, Silkscreen, and Surface Finish: Protects the board and makes it last longer.
These parts help the PCB support and connect electronic components. Without them, modern electronics wouldn’t work.
Key components of a PCBA
A printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) has many important parts. These parts work together to make the board function. Each part has a job to ensure the assembly works correctly. Knowing these parts shows how detailed and precise PCBA manufacturing is.
Here are the main parts usually found in a PCBA:
Component | Description |
|---|---|
A list of all electronic parts needed for the PCBA. It includes details like brand, type, amount, and where each part goes. | |
Coordinate File | A file with exact locations for placing parts on the PCB. This file helps machines place parts in the right spots during assembly. |
Customer-Provided Samples | Optional examples from customers to guide the assembly team. These samples help ensure correct part placement and soldering, especially for large orders. |
Process Guidance Documentation | Papers with special instructions or design rules for assembly. These make sure the final product meets quality and design needs. |
Test Documentation | A guide for testing the finished boards. It lists steps and checks to confirm the PCBA works well and is reliable. |
The Bill of Materials (BOM) is like a plan for the whole assembly. It makes sure every part is included and matches the design. The Coordinate File is key for machines to place parts exactly where they belong. For custom projects, customer-provided samples can help avoid mistakes during assembly.
Process guidance documentation gives clear instructions for building complex designs. Test documentation is very important to check if the PCBA works as it should. Without testing, the PCBA might not be reliable.
All these parts help the PCBA work properly. By putting them together, a simple PCB becomes a working PCBA. This change shows a big difference between PCB and PCBA. A PCBA adds parts to make a complete system.
💡 Tip: Always include clear instructions and testing in your PCBA process. This reduces mistakes and ensures high-quality results.
PCBA Manufacturing Meaning and PCB Production
PCB manufacturing process
The pcb manufacturing process changes raw materials into working circuit boards. First, you design the board layout using special software. This makes sure the copper lines and part placements match your needs. Once the design is ready, the building process begins.
Main steps include:
Etching: Cuts away extra copper to form pathways.
Drilling: Makes holes for parts and connections.
Plating: Covers copper lines with a protective layer.
Surface finishing: Adds solder masks and labels for assembly.
Here’s a detailed process:
Step | Description |
|---|---|
Design and Prototyping | Use software to create layouts and make test boards. |
Material Selection | Pick base materials and copper thickness for good performance. |
PCB Fabrication | Print designs, etch, drill, and add plating and finishes. |
Assembly | Attach and solder parts onto the board. |
Testing and Quality Assurance | Check the board to ensure it works and has no defects. |
This process creates a printed circuit board, which is ready for the next steps in assembly.
PCBA manufacturing process
The pcb assembly process turns a PCB into a working circuit board assembly. First, solder paste is added to the board using stencils. Then, machines place parts like resistors and capacitors onto the board.
Steps include:
Adding solder paste to the board pads.
Checking the paste with 3D optical tools.
Placing parts using robotic machines.
Heating the board in a reflow oven to melt the paste.
Inspecting the board with automated tools.
Repeating for double-sided boards if needed.
Doing manual work for tricky designs or small batches.
Each step ensures the printed circuit board assembly works properly. Testing confirms it is reliable before use.
Tools and techniques for PCB vs PCBA
Different tools and methods are used for PCB and PCBA processes. PCB production makes the board, while PCBA adds parts to make it work.
Process/Technique | Description |
|---|---|
PCB Layer Division and Assembly | Cuts copper lines, drills holes, and adds solder masks for safety. |
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Uses stencils for solder paste and machines to place parts. |
Reflow Soldering | Heats solder paste in an oven to secure parts. |
Through-Hole Soldering | Uses wave or selective soldering for strong connections. |
Inspection Techniques | Includes visual checks, automated inspections, and X-rays for quality. |
These tools and methods help make high-quality PCBs and PCBAs. Knowing their differences can improve your manufacturing process and results.
💡 Tip: Automated tools like AOI can improve quality checks for both PCB and PCBA production.
Quality control in PCB and PCBA production
Quality control is very important for making reliable PCBs and PCBAs. Without proper checks, devices might fail, causing safety problems or expensive fixes. Strong quality checks help meet standards and create good products.
Different steps ensure PCB and PCBA quality. For PCBs, checks focus on the board’s design and connections. Tools like automated optical inspection (AOI) find issues like broken lines or misplaced layers. For PCBAs, checks are more detailed. They confirm parts are placed and soldered correctly so the board works as planned.
Here are common quality control steps for PCB and PCBA:
Quality Control Process | Description |
|---|---|
Solder Paste Inspection | Checks if solder paste is applied correctly before adding parts. |
Automated Optical Inspection | Uses cameras to find missing or wrongly placed parts. |
X-ray Inspection | Looks at BGA part connections without damaging the board. |
Functional Circuit Testing | Tests if the PCBA works in real-world-like conditions. |
In-Circuit Testing | Checks each circuit to make sure it works properly. |
In fields like aerospace and medical devices, quality is even more important. PCBAs must follow strict rules, like IPC class 2 or 3, to stay safe and reliable. Poor quality in these areas can cause big problems, so careful checks are a must.
Testing during PCBA production is also key. Functional testing makes sure the board works as it should in real-life situations. In-circuit testing looks at each circuit for problems. These tests help avoid failures and make products more dependable.
Focusing on quality control improves PCB and PCBA safety and performance. It also helps meet industry rules and builds customer trust.
💡 Tip: Use tools like AOI and X-ray systems to make quality checks faster and more accurate.
Key Differences Between PCB and PCBA in Functionality
Functional role of PCB
A PCB is like the backbone of electronic gadgets. It holds parts together and helps send signals between them. Think of it as the nervous system, carrying messages to make everything work smoothly.
The main job of a PCB is to support circuits and let parts communicate. Testing is very important to check if the PCB works correctly in real-life situations.
Here’s how PCB functionality is checked:
Circuit Testing: Engineers test the board in fake conditions to ensure it works.
Signal Transmission: Copper lines on the PCB carry signals between parts.
Fixture Design: Special tools are made for testing many boards quickly.
Each PCB is different, so testing methods are customized. This ensures the board works well with other parts in the device.
💡 Tip: Always test PCBs during production to find problems early. This ensures they work as planned.
Functional role of PCBA
A PCBA turns a plain PCB into a working system. By adding parts like resistors and chips, it becomes the brain of the device. It handles signals, calculations, and controls based on its design.
The PCBA’s job depends on careful assembly and testing. Machines place parts in the right spots, and robotic arms solder them perfectly. This reduces mistakes and makes the PCBA more reliable.
Key PCBA functions include:
Signal Processing: Parts on the PCBA work together to handle signals.
Operational Control: It manages tasks, from simple to complex ones.
Quality Assurance: Tests ensure the PCBA works well in different situations.
By adding parts to the PCB, the PCBA becomes a complete system that can do its job.
🔍 Note: Using machines for assembly makes PCBAs more accurate and dependable.
How functionality evolves from PCB to PCBA
The change from PCB to PCBA is a big step. A PCB starts as a simple board for circuits. When parts are added, it becomes a PCBA that can do complex tasks.
This change involves several steps:
Component Placement: Machines put parts like resistors on the PCB.
Soldering: Robotic arms attach parts securely with solder.
Testing: Tests check if the PCBA works as it should.
Automation helps make this process faster and cheaper. Machines place parts exactly, and ovens secure them with heat.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Reduced Costs | |
Increased Flexibility | Change parts easily as the design improves, saving time. |
Minimized Waste | Fix errors early on the bare board to save materials. |
The shift from PCB to PCBA shows how functionality grows. A PCB gives the structure, while a PCBA adds parts to make it work. Both are important in making electronic devices.
💡 Tip: Use expert reviews and machines to ensure a smooth switch from PCB to PCBA. This improves quality and saves time.
Cost and Time Considerations in PCB vs PCBA
Cost factors for PCB
Making a PCB costs more if the board is big. Bigger boards need extra materials and take up more space, raising costs. The number of layers also matters. Boards with more than two layers are harder to make and cost more.
The type of material used affects the price too. Common materials like FR-4 are cheaper, but special ones cost a lot more. Tiny holes and many drills also increase costs because they need careful work. If you need the board quickly, the price goes up due to the rush.
Factories track these costs in reports. These reports show setup costs, running expenses, and profits. This helps explain how production costs affect the final price.
Cost Factor | Description |
|---|---|
Board Size | |
Layer Count | Extra layers make the board harder and pricier to build. |
Material Type | Special materials cost more than regular ones like FR-4. |
Drill Size and Count | Tiny holes and many drills need extra care and cost more. |
Lead Time | Faster delivery means higher costs. |
Cost factors for PCBA
The cost of a PCBA depends on materials, design, and quantity. Using better materials makes the board last longer but costs more. Complicated designs need careful work, which can lead to mistakes and higher costs. Making more boards at once lowers the cost per board, but starting production is still expensive.
PCBA costs also include assembly, testing, and fixing mistakes. If the PCB is poor quality, it can make assembly harder and waste materials. Spending on good materials and processes saves money over time.
💡 Tip: Choose smart designs and materials to save money without losing quality.
Time requirements for PCB and PCBA
The time to make a PCB or PCBA depends on the design and project needs. Making a PCB involves steps like cutting, drilling, and coating, which usually take 1–2 weeks. Adding parts and testing for a PCBA takes extra time. Managing the list of parts (BOM) can slow things down too.
Double-sided boards and programming machines make the process longer. On average, making a PCBA takes 2–3 weeks. If you need it faster, it costs more.
🔍 Note: Plan ahead to avoid delays and extra costs.
Tips to save money and time
Saving money and time in pcb and pcba production needs good planning. Smart choices can make work faster and cheaper without losing quality. Here are some easy tips to help:
Use Automation: Machines can do tasks like soldering quickly and correctly. For example, Company A used automation to finish assembly faster and boost output.
Try AI Tools: AI can find mistakes early, cutting waste and improving reliability. Company B used AI checks to make customers happier by reducing errors.
Work with Designers: Team up with designers to make pcb layouts easier to build. Company D worked this way and made production faster and cheaper.
Study Production Data: Look at data to find slow steps or problems. Company E used data to fix issues and make work faster.
Go Green: Using eco-friendly materials saves money and helps the planet. Company C went green and gained more customers while helping the environment.
Company | Strategy Used | Results Achieved |
|---|---|---|
Company A | Automation | Faster assembly, better accuracy, higher output |
Company B | AI Inspections | Fewer mistakes, better reliability, happy clients |
Company C | Eco-Friendly Methods | Lower impact, more customers, better reputation |
Company D | Design Collaboration | Quicker production, lower costs, faster delivery |
Company E | Data Analysis | Fixed problems, faster work, fewer defects |
Using these ideas can make your pcb and pcba processes better. You’ll save time, cut costs, and still get great results.
💡 Tip: Keep checking your methods and try new tools to stay ahead in electronics manufacturing.
Applications and Use Cases of PCB and PCBA
Common uses of PCBs
PCBs are the base of most modern electronics. They hold and connect parts in many devices. You’ll find them in almost every gadget you use daily. Here are some examples:
Medical Devices: Used in machines like ECGs, CT scanners, and health trackers.
LED Lighting: Help manage heat so LEDs last longer and work better.
Consumer Electronics: Found in phones, tablets, and smart home gadgets.
Industrial Equipment: Used in factory machines that work in tough conditions.
Automotive Components: Found in car engines and entertainment systems.
Aerospace and Maritime Applications: Used in satellites, airplane systems, and ship devices.
These examples show how PCBs are key to many technologies, helping industries grow.
Common uses of PCBAs
PCBAs make PCBs useful by adding parts that let them work. They are the “brains” of many devices we use. Here are some examples:
Telecommunications: Found in routers, switches, and signal amplifiers.
Medical Equipment: Used in heart monitors, CT scanners, and blood pressure devices.
Automotive Systems: Found in car engines, GPS, and audio systems.
Aerospace Technology: Used in airplane lights, radios, and monitoring tools.
Consumer Electronics: Found in phones, computers, and TVs for advanced features.
By adding components, PCBAs turn simple PCBs into working systems for modern devices.
Industry-specific examples
PCBs and PCBAs are used in many industries, showing their flexibility. Below is a table with examples from different fields:
Industry Sector | |
|---|---|
Automotive Electronics | Control systems, entertainment, safety, and electric vehicle tech. |
Industrial Controls & Robotics | Automation, motion control, and smart factory upgrades. |
Medical Equipment | Imaging machines, surgical robots, and patient monitors. |
5G Infrastructure | Fast networks and smart device ecosystems. |
Avionics | Flight systems, engine tracking, and critical electronics. |
For instance, the Apple iPhone X uses a PCBA with the A11 chip for better speed and energy use. Similarly, the iLimb prosthetic hand uses a PCBA for smooth control, helping people with limb loss.
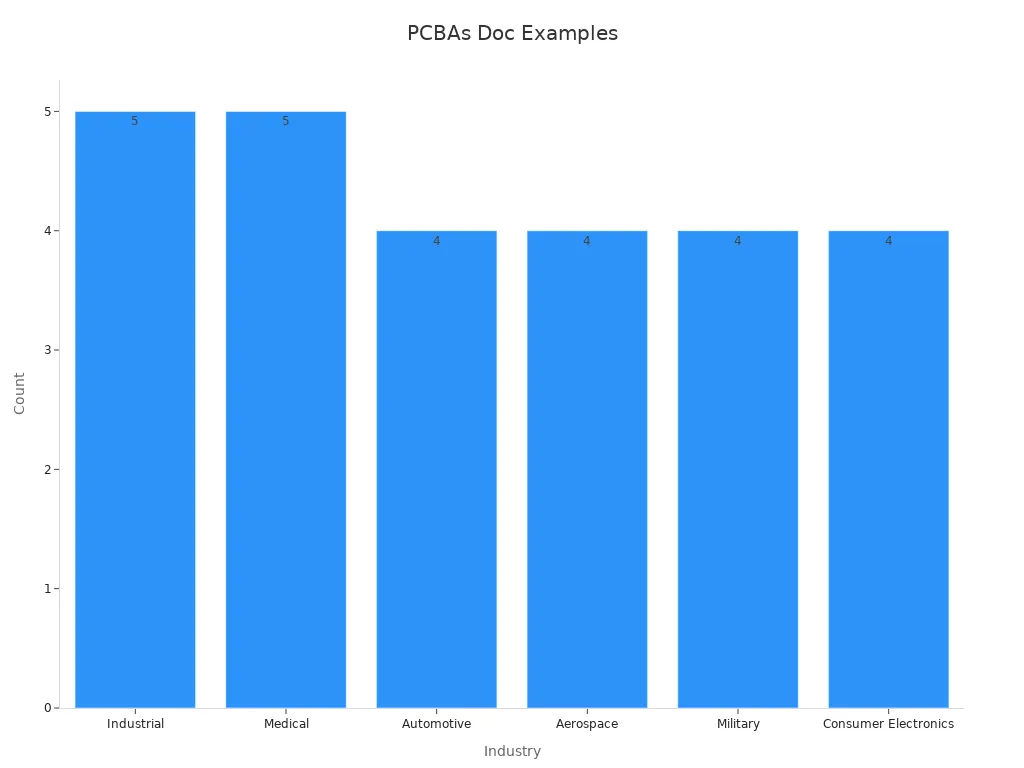
These examples prove how PCBs and PCBAs are customized for different industries, driving progress and efficiency.
When to Choose PCB vs PCBA
When to Use a PCB
Pick a PCB when your project is in the early stages. It’s great for testing designs and fixing problems before adding parts. This saves time and money by catching mistakes early. For example, in big environmental projects like the Hudson River PCB Cleanup, engineers checked the PCB’s structure first before moving to advanced assemblies.
Here’s a table with real-world examples:
Case Study | Description |
|---|---|
Hudson River PCB Cleanup | Removed PCB pollution from river sediments at a major U.S. cleanup site. |
New Bedford Harbor PCB Cleanup | Cleaned up PCB-contaminated sediments in the harbor and nearby areas. |
Kalamazoo River PCB Cleanup | Focused on removing PCBs from riverbeds, flood zones, and old paper mills. |
Fox River PCB Cleanup | Dredged and capped PCB-contaminated sediments in the Lower Fox River. |
These examples show how PCBs are used for testing and structural checks.
When to Use a PCBA
Choose a PCBA when you need a fully working circuit board. PCBAs are perfect for finished products or advanced testing. For example, PCBAs power devices like smartphones and laptops in consumer electronics. They are also vital in medical tools where accuracy and reliability are key.
With a PCBA, you get a ready-to-use board with all parts included. This makes it easier to test in real-life situations. PCBAs are also important in industries like aerospace and cars, where safety and performance matter most.
Things to Think About
When deciding between PCB and PCBA, think about cost, factory ability, and speed. Cost is important, especially for small businesses. Make sure the factory can handle your design. Speed matters if you’re on a tight schedule. Other things like quality checks, location, and customer service also count.
For example, a factory with good quality checks can make reliable PCBAs. A nearby factory can ship faster. These factors help you pick what fits your project best.
💡 Tip: Think about your project’s stage and needs to decide between PCB and PCBA.
Knowing the difference between PCB and PCBA helps in electronics. A PCB is the base, giving support and connecting parts. A PCBA turns the PCB into a working system by adding components.
Aspect | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | A plain board with copper connections | A board with parts added, making it functional |
Function | Supports and connects electronic parts | Performs tasks based on its design |
Testing | Checks for broken or missing connections | Tests if the board works as a complete system |
Applications | Best for testing and early designs | Used in finished devices like phones and medical tools |
Use a PCB for testing or trying out ideas. Pick a PCBA when you need a ready-to-use board. Always think about your project’s needs, budget, and time to decide wisely.
💡 Tip: Work with your team to match designs with production needs. This helps make better and more reliable products.
FAQ
What’s the main difference between a PCB and a PCBA?
A PCB is just a plain board with copper lines. A PCBA has all the parts added to make it work. The PCB gives support, while the PCBA does the actual job in a device.
Can a PCB be reused after removing parts?
Yes, you can reuse a PCB if it’s not damaged. The board must stay in good shape during part removal. Always check for problems before using it again.
Why is quality control important for PCB and PCBA?
Quality control makes sure the PCB and PCBA are safe and work well. It stops mistakes, lowers failures, and makes them more reliable. This is very important in fields like medicine and aerospace.
How does automation help in PCBA production?
Automation makes assembly faster and more accurate. It reduces mistakes and places parts perfectly. It also cuts costs and makes the process smoother and more reliable.
Which industries use PCBAs the most?
Industries like telecom, cars, medicine, and aerospace need PCBAs. They power things like phones, medical tools, car systems, and airplane electronics.
💡 Tip: Pick a trusted maker for your PCB and PCBA to get the best quality.
See Also
Uncovering The Subtle Variations Between PCBA And PCB
Examining The Functional And Structural Distinctions Of PCBA And PCB
Understanding PCBA Services And Their Importance In Electronics Production