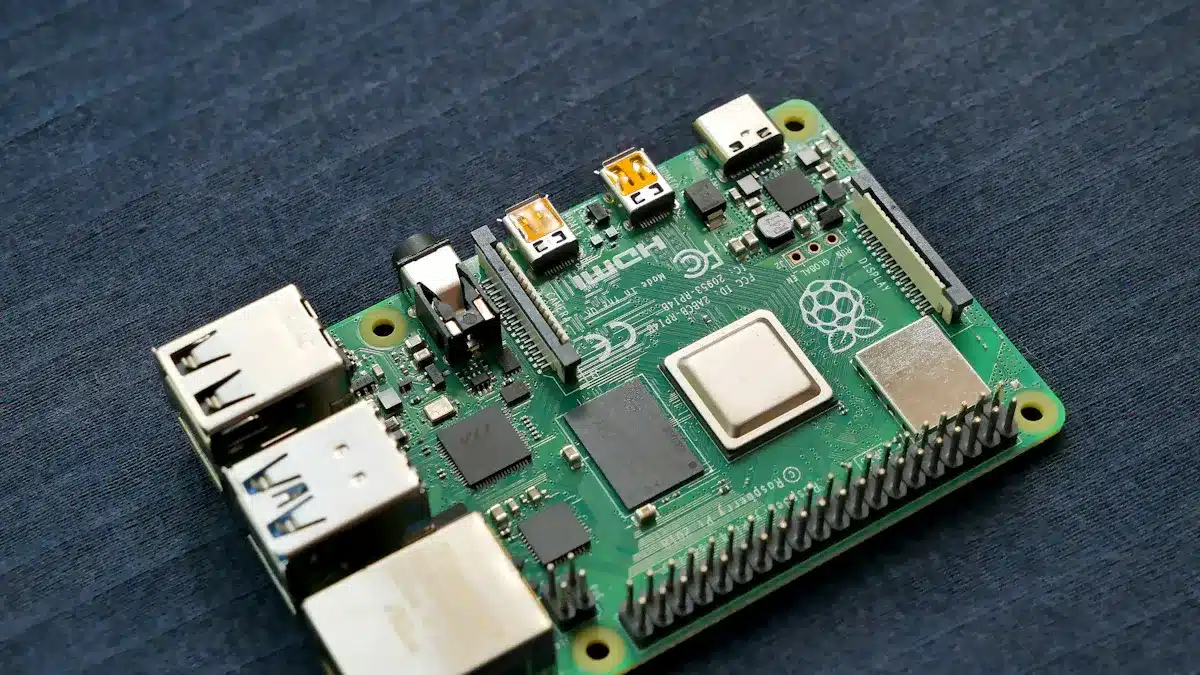

Printed circuit boards (PCBs), which is the pcb full form, are important for running electronics daily. These flat boards, made from materials that don’t conduct electricity, hold tiny paths that connect parts like resistors, capacitors, and chips. In 2023, more people needed PCBs because of 5G and IoT tech, even with problems like supply chain delays. This shows how useful they are in things like gadgets and cars. The PCB market might grow to $120 billion by 2030, showing how key they are for new ideas today.
Key Takeaways
PCBs, or Printed Circuit Boards, link electronic parts in devices like phones and cars.
The PCB market is growing fast and may reach $120 billion by 2030, thanks to new tech like 5G and IoT.
PCBs have types like single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer, each used for different electronic needs.
PCBs help make devices smaller, stronger, and more reliable, perfect for modern gadgets and machines.
Learning about PCBs shows how they power everyday tech, from gadgets to medical tools.
PCB Full Form and Definition
What Does PCB Stand For?
PCB means “Printed Circuit Board.” It is a common term in electronics. You might hear it when talking about gadgets or cars. The PCB card full form shows its importance in modern devices. Without it, many devices wouldn’t work well or be small.
PCBs are important because they link parts like resistors and chips. These links use special paths to let electricity flow smoothly. This setup helps devices do hard tasks while staying small and light.
What Is a Printed Circuit Board?
A printed circuit board is flat and made of layers. These layers include materials that conduct and block electricity. It holds and connects all the needed parts in a device. Think of it as a map where paths lead to parts. These paths guide electricity so the device works properly.
Here’s a table to explain PCBs better:
Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
Definition | A printed circuit board (PCB) has layers of conductive and insulating materials. |
Importance | Found in almost all electronics, linking parts together. |
Market Growth |
The need for PCBs keeps growing. From 2017 to 2021, the industry grew by 6.14%. By 2024, the market could reach $82.25 billion. By 2033, it might grow to $121.34 billion. These numbers show how PCBs help new technology grow.
Tip: When using your phone or laptop, remember a PCB is making it work!
History and Evolution of PCBs
The Invention of the Printed Circuit Board
The printed circuit board (PCB) changed how electronics were made. In 1907, Leo Hendrik Baekeland improved phenolic resin, a key PCB material. Then in 1925, Charles Ducas printed circuit patterns on insulating materials. This idea led to smaller and better electronic devices.
Dr. Paul Eisler was very important in PCB history. In 1936, he made the first working PCB for radios using foil. By 1942, he created the first double-sided PCB, making circuits smaller. In 1948, the U.S. approved PCBs for commercial use, helping them become popular.
Fun Fact: Early PCBs were used in the military before consumer electronics.
Key Milestones in PCB Development
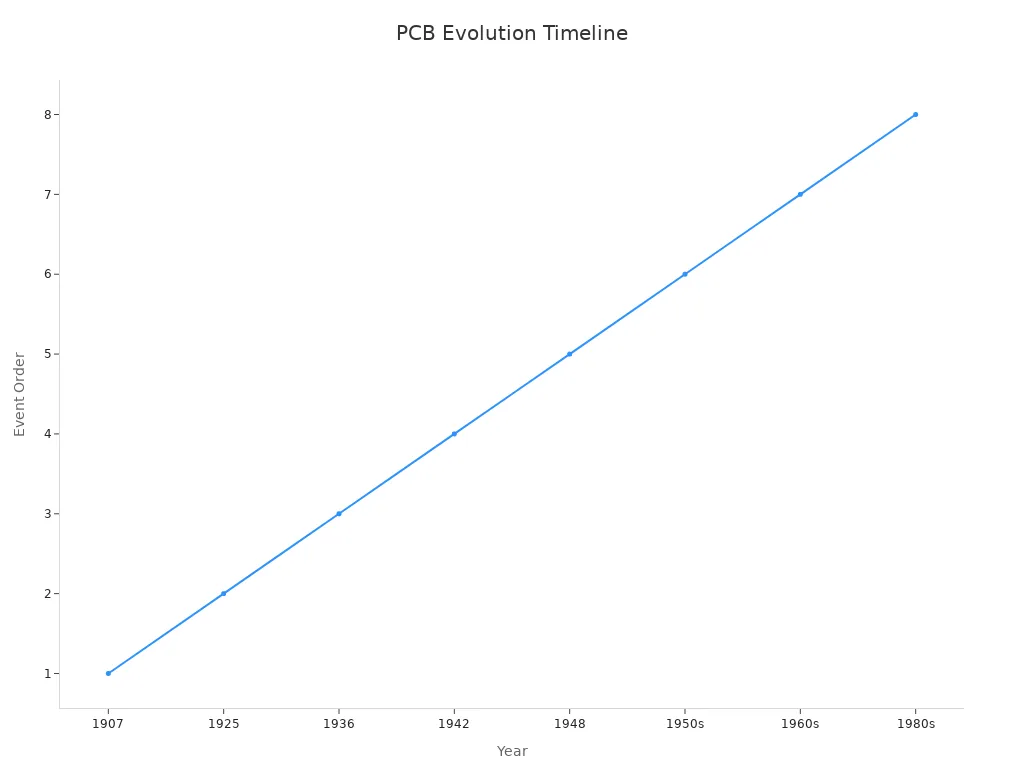
PCBs have been improving for over 100 years. Here’s a timeline of important events:
Year | Key Person/Event | Importance |
|---|---|---|
1907 | Leo Hendrik Baekeland | Made phenolic resin better, vital for PCBs. |
1925 | Charles Ducas | Printed circuits on insulating materials. |
1936 | Paul Eisler | Created the first PCB for radios using foil. |
1942 | Paul Eisler | Made the first double-sided PCB for compact circuits. |
1948 | United States | Approved PCBs for commercial use. |
1950s | Various | Switch from tubes to transistors increased PCB use. |
1960s | Various | Double-sided and multilayer PCBs were introduced. |
1980s | Various | Smaller parts boosted PCB demand. |
In the 1980s, surface mount technology replaced older methods. This made PCBs smaller and more useful for modern devices. By the 2000s, high-density PCBs became key for smartphones and small gadgets.
Note: Every step in PCB history helped create today’s advanced electronics, like phones and medical tools.
Features and Types of PCBs
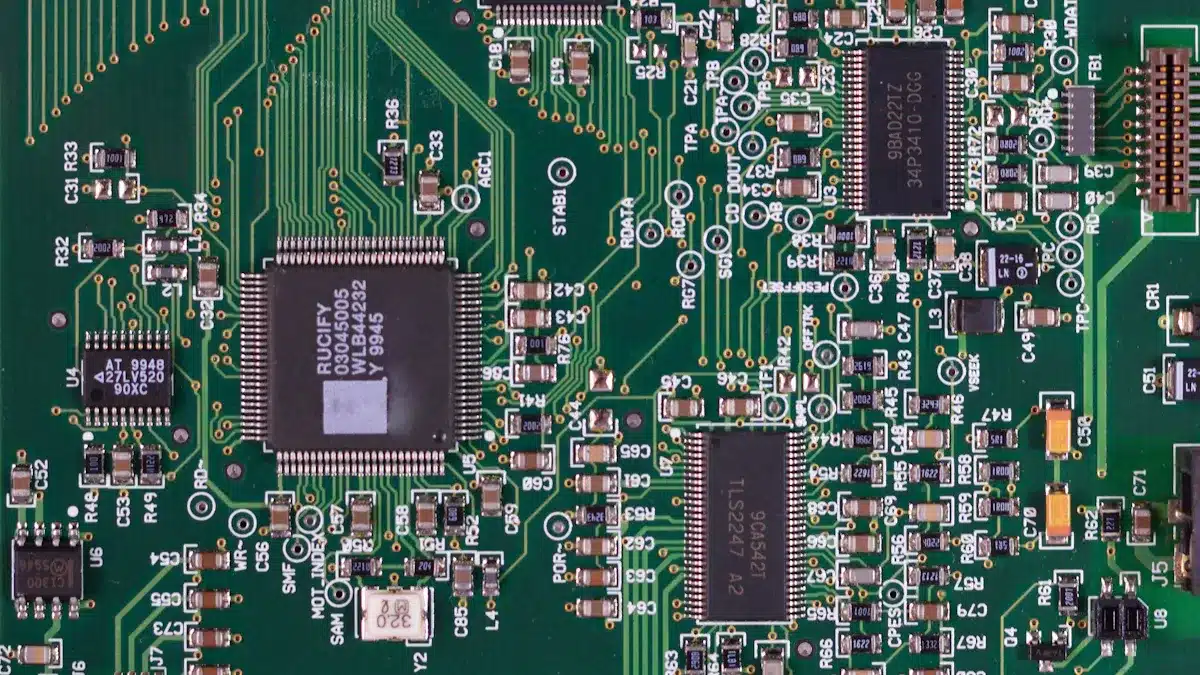
Key Features of a PCB
Printed circuit boards, or PCBs, are crucial in today’s gadgets. They are found in almost everything, like phones and medical tools. Their design helps connect parts while keeping devices small. Here are some important features of PCBs:
Compact Design: PCBs fit many circuits into tiny spaces. This makes devices lighter and easier to carry.
Durability: Materials like fiberglass and epoxy make PCBs tough. They resist damage from wear and the environment.
Ease of Assembly: PCBs make it simple to connect parts. This saves time and lowers production costs.
Reliability: The paths on PCBs keep electricity flowing steadily, even in tough conditions.
The PCB market shows how valuable they are. In 2023, it was worth $67.9 billion. By 2029, it could grow to $92.4 billion. New tech like self-driving cars and 5G networks need advanced PCBs, driving this growth.
Tip: Next time you use your phone, remember a PCB is making it work!
Types of PCBs (Single-Sided, Double-Sided, Multilayer)
Knowing the types of PCBs helps you see their uses. Each type is made for specific needs and designs.
Single-Sided PCBs: These are the easiest and cheapest to make. Parts go on one side, and pathways are on the other. They’re used in simple things like LED lights and calculators.
Double-Sided PCBs: These have parts and pathways on both sides. This allows more circuits and is common in electronics and car systems.
Multilayer PCBs: These have several layers stacked together. They are used in complex devices like computers, smartphones, and medical machines.
Other types include Rigid PCBs, which stay firm, and Flexible PCBs, which bend to fit tight spots. Rigid-Flex PCBs mix both, making them useful for many tasks.
The PCB market is growing fast, with a 5.4% yearly increase expected from 2024 to 2029. As technology improves, the need for smaller and smarter PCBs will rise.
Advantages and Limitations of Printed Circuit Boards
Benefits of Using PCBs
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) have many benefits for modern electronics. Their small size lets them fit many parts in tight spaces. This helps make lightweight and portable devices like phones and tablets. PCBs are great for advanced tech, such as medical tools and smartphones.
They are made using a standard process, so they are reliable. You can trust them to work well in gadgets and machines. Their design reduces signal problems, keeping devices running smoothly without interference.
PCBs are easy to put together. Parts can be connected quickly, saving time and money. They are also strong and last long, even in tough conditions.
Here’s why PCBs are useful:
They are perfect for high-tech gadgets.
They allow complex designs with many layers.
They handle lots of parts in small spaces.
Tip: Think of a PCB as a map that guides electricity, helping your devices work properly.
Common Drawbacks of PCBs
PCBs have some downsides too. They are not the best for very dense circuits or super high-performance needs. For example, simpler boards like printed wiring boards (PWBs) are used in cheap gadgets and learning kits.
Making PCBs can cost a lot for small projects. If you need quick changes, their fixed design can be a problem. Once made, it’s hard to change their layout.
PCBs can also harm the environment. Materials like fiberglass and epoxy are not always eco-friendly. Throwing away old PCBs adds to electronic waste, which is bad for nature.
Here’s a quick comparison:
PCBs: Best for advanced gadgets and layered designs.
PWBs: Better for cheap and simple uses.
Note: Knowing both the good and bad sides of PCBs helps you pick the right option for your project.
Applications of PCBs in Different Industries
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are crucial for many industries. They help modern devices and systems work properly. Their flexibility and usefulness make them essential in electronics, cars, and healthcare.
Consumer Electronics
You use PCBs every day in your gadgets. Devices like phones, laptops, and gaming consoles need PCBs to work. These boards let makers create small and light devices by combining many parts on one board. This has changed how we use technology.
The global PCB market is growing fast. In 2023, it was worth $67.9 billion. By 2029, it might reach $92.4 billion. This growth is due to 5G devices becoming popular. 5G networks need advanced PCBs to handle faster speeds and more data. These boards keep your devices connected and working well.
Fun Fact: Without PCBs, your gadgets would be bigger and less reliable.
Automotive Applications
Today’s cars rely on PCBs for their smart features. PCBs power things like music systems and electric engines. They also help with safety features like airbags and driver assistance systems (ADAS), making driving safer.
The car PCB market was worth $9.79 billion in 2023. It is expected to grow by 5.7% each year until 2030. This is because of the rise of electric cars (EVs) and smarter car tech. EVs need advanced PCBs for battery and engine control. ADAS uses high-tech boards to process data for safety.
Main uses of PCBs in cars:
Electric engines in EVs.
Music and navigation systems.
Safety tools like ADAS and airbags.
As cars get smarter, the need for better PCBs will grow.
Medical Devices
In healthcare, PCBs are key for accurate and reliable devices. They help machines like MRI scanners, pacemakers, and glucose monitors work. These devices use PCBs to process data and give correct results, improving patient care.
More hospitals now use automated tools, increasing the need for multilayer PCBs. These boards handle complex circuits for robots and medical tools. For example, robotic surgery systems use PCBs to perform precise operations.
Tip: When you visit a hospital, remember PCBs power the tools that help doctors.
The global PCB market was worth $75 billion in 2021. By 2030, it could grow to over $128 billion. This shows how important PCBs are for improving medical technology and healthcare.
Aerospace and Defense
Precision and reliability are very important in aerospace and defense. Advanced systems keep these industries safe and efficient. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are key to making this happen. They are the base for electronics in planes, satellites, and military gear.
PCBs in aerospace must handle tough conditions. High altitudes, strong vibrations, and temperature changes need sturdy designs. Makers use special materials like heat-resistant laminates and copper alloys. For example, airplane systems use PCBs for navigation, communication, and controls.
In defense, PCBs power radars, missile systems, and communication tools. These boards must work perfectly in critical moments. Multilayer PCBs are used because they fit complex circuits in small spaces. Flexible PCBs are also common. They fit tight spots and make equipment lighter.
Fun Fact: The International Space Station uses PCBs for communication and life support. Without them, astronauts couldn’t stay connected or survive in space.
The need for PCBs in aerospace and defense is growing. New technology means more advanced systems will use these boards. From drones to space missions, PCBs are shaping the future of these fields.
Industrial Equipment
Factories and machines depend on PCBs to work well. You’ll find them in robots, machinery, and control systems. They help automate tasks, reduce mistakes, and boost productivity.
PCBs in factories must survive tough environments. Dust, moisture, and heat can cause problems. Makers use coatings and strong materials to protect them. For example, conformal coatings stop corrosion and electrical issues.
Robots are one area where PCBs are very useful. They control robotic arms in factories. These boards process sensor data and guide movements. Without PCBs, robots wouldn’t be as advanced as they are now.
Another example is power systems. PCBs manage voltage and current in machines. They help machines run smoothly and find problems early.
Tip: When you see a robot building cars or packing items, remember a PCB is making it work.
The industrial PCB market is growing fast. Smart factories and automation need better PCBs. Expect more new ideas in this area as technology improves.
Printed circuit boards are key to making electronic devices work. They help improve technology and make it more efficient. You use them every day in things like phones, cars, and medical tools. Their ability to do many tasks makes them important in many industries.
The PCB market is growing fast and could reach $120 billion by 2032. This growth is due to the need for smaller, smarter gadgets and better PCB designs. In cars, PCBs are vital for electric engines and self-driving features. This shows how they help create the future of technology.
Tip: Knowing the pcb full form and why it matters helps you see how printed circuit boards power the devices you use daily.
FAQ
What is the difference between a PCB and a PWB?
A PCB links electronic parts, while a PWB focuses on wiring. PCBs are used in advanced gadgets. PWBs are simpler and cheaper, great for basic devices.
Why are multilayer PCBs important?
Multilayer PCBs fit many circuits in small spaces. They are used in phones, computers, and medical tools. Their layers boost performance and save space, making them vital for modern gadgets.
Can PCBs be recycled?
Yes, but recycling PCBs is hard. Special methods recover metals like copper and gold. Recycling helps reduce waste and protects the environment.
How do flexible PCBs differ from rigid PCBs?
Flexible PCBs can bend to fit tight spots. Rigid PCBs stay solid and firm. Flexible ones are great for wearables, while rigid ones suit strong machines.
What materials are used to make PCBs?
PCBs use fiberglass for strength and copper for electricity flow. Epoxy resin keeps circuits safe from harm. These materials make PCBs strong and reliable for electronics.
See Also
Understanding PCBA Abbreviation and Its Significance in Electronics
Defining PCB Design and Its Importance in Electronics
The Meaning of PCBA and Its Importance Explained
Exploring PCBA Definition and Its Essential Uses in Electronics