Circuit circuit boards are very important in today’s technology. They act like the main support for electronic devices, connecting different parts and helping them work together. Learning about the different types of circuit circuit boards can help you pick the best one for your project. The worldwide market for printed circuit circuit boards was worth USD 72.99 billion in 2024 and is expected to grow to USD 97.88 billion by 2032. This growth shows that more industries need them, like consumer electronics and cars. By understanding the special features and uses of each type, you can make smart choices for your designs.
Key Takeaways
Learn about the different types of circuit boards. These include single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, rigid, flexible, rigid-flex, HDI, and LED boards.
Pick single-sided boards for simple projects. They are cheap and easy to use.
Choose double-sided boards when you need more parts in a small space. This is especially true for consumer electronics.
Use multi-layer boards for advanced uses. They are best when space is tight and performance matters.
Think about flexible circuit boards for devices that need to bend. They work well for wearables and smartphones.
Single-Sided Circuit Boards
Overview
Single-sided circuit boards are also known as single-layer PCBs. They have a simple design. All parts are on one side. The other side is empty. This easy layout makes them simple to make and put together.
Here are some key features of single-sided circuit boards:
Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
Simple Design | Have a clear design, with parts on one side only. |
Limited Complexity | Less complicated, good for simple electronics with fewer parts. |
Cost-effective | Cheaper to make, great for projects with tight budgets. |
Applications
Single-sided circuit boards are used in many areas. Their simplicity and low cost make them a favorite for many devices. Here are some common items that use single-sided circuit boards:
Consumer electronics: Calculators, remote controls, radio receivers, and LED lights.
Power supplies: Relays and solid-state power converters.
Industrial sensors and controls.
Automotive uses: Dashboard switches and basic sensors.
Educational kits and hobby projects (like Arduino shields for beginners).
Vending machines and home appliances.
You can see that single-sided circuit boards are important in daily technology. Their low cost and ease of use make them great for projects that don’t need much complexity. Whether you are making a simple device or working on a hobby, single-sided circuit boards can work well for you.
Double-Sided Circuit Boards
Overview
Double-sided circuit boards are also called double-layer PCBs. They are more complex than single-sided boards. You can find conductive pathways on both sides of these boards. This allows for more components, making them good for advanced electronics.
Here’s a quick comparison of single-sided and double-sided circuit boards:
Feature | Single-Sided PCB | Double-Sided PCB |
|---|---|---|
Conductive Layers | One side only | Both sides |
Complexity of Design | Less complex, lower component density | More complex, higher component density |
Fabrication Difficulty | Easier to fabricate | More difficult due to complexity |
Applications | Basic electronics (e.g., calculators) | Advanced electronics (e.g., LED systems) |
Applications
You can find double-sided circuit boards in many uses because they are versatile. They are great for devices needing more parts in a small space. Here are some common uses:
Consumer Electronics: Many gadgets, like smartphones and tablets, use double-sided PCBs for their detailed designs.
LED Systems: These boards meet the high-density needs of LED lighting, helping with heat dissipation.
Communication Devices: Routers and modems use the extra space for parts, improving performance.
Automotive Applications: Modern cars use double-sided PCBs for features like navigation systems and infotainment units.
The benefits of double-sided circuit boards make them popular in many fields. They give more space for parts, allowing for complex designs without making the board bigger. Also, they are cheaper than multilayer PCBs, making them a smart choice for many projects.
Multi-Layer Circuit Boards

Overview
Multi-layer circuit boards have many layers of pathways. These layers stack on top of each other, making a small design. Some multi-layer PCBs can have up to 40 layers in advanced electronics. This high number of layers helps engineers make powerful boards that are still small.
Multi-layer designs have many benefits:
Higher Component Density: More parts can fit in a smaller space. This is important for making things smaller.
Improved Signal Integrity: Multi-layer boards help devices work better by cutting down interference.
Reduced Footprint: Their small size is key for modern uses.
For instance, modern smartphones can hold over 1,000 parts in a PCB area smaller than 100 cm². This shows how miniaturization affects today’s technology.
Applications
Multi-layer circuit boards are used in many high-tech fields. Here are some main uses:
Telecommunications Equipment: Devices like satellites and mobile phones need multi-layer PCBs for strength and function.
Medical Equipment: Important for devices like X-rays and heart monitors, these boards are small and work well.
Military and Defense Equipment: Fast circuits in military gear need to be very strong and functional.
Automotive: Multi-layer PCBs are used in parts like GPS and engine sensors, known for saving space and resisting heat.
Aerospace: Important for computers in control rooms and cockpits, built to handle tough conditions.
Industrial Equipment: Used in control systems and machines, appreciated for their strength in tough environments.
Also, multi-layer circuit boards are important in science and research, home appliances, and security systems. Their small design and better performance make them a popular choice in many areas.
Rigid Circuit Boards
Overview
Rigid circuit boards, also known as rigid PCBs, have a strong structure. They can have one layer or many layers of pathways that conduct electricity. These boards do not bend or flex. This makes them good for many uses. You can find rigid PCBs in many electronic devices because they are tough and reliable.
Here are some important features of rigid circuit boards:
Stability: They give a steady base for parts, which helps them work well.
Durability: Rigid PCBs can resist damage from the environment, so they last a long time.
Cost-Effectiveness: They usually cost less to make than flexible or multilayer boards.
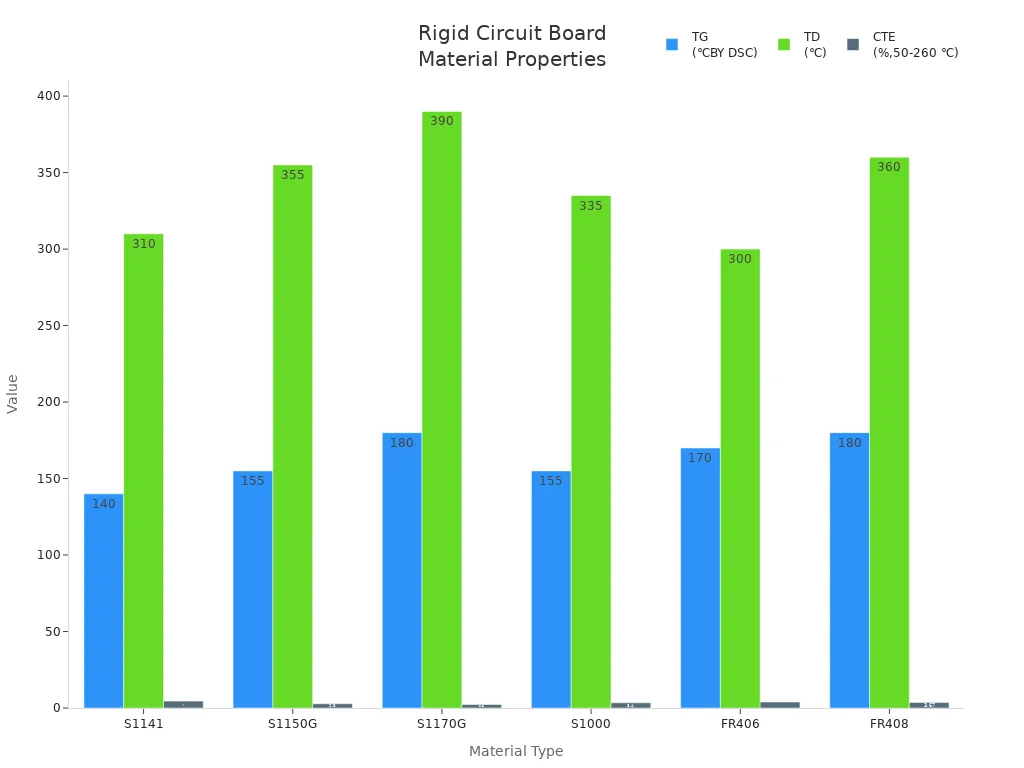
The materials used in rigid circuit boards are very important for how they work. Common materials include FR-4, which is a type of glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. Below is a table showing some common materials used in rigid circuit boards and their thermal properties:
Material Type | TG(℃BY DSC) | TD(℃) | CTE(%,50-260 ℃) |
|---|---|---|---|
S1141 | 140 | 310 | 4.5 |
S1150G | 155 | 355 | 2.8 |
S1170G | 180 | 390 | 2.3 |
S1000 | 155 | 335 | 3.4 |
FR406 | 170 | 300 | 3.93 |
FR408 | 180 | 360 | 3.67 |
Applications
Rigid circuit boards are used in many industries. Their strength and reliability make them good for different applications. Here are some common uses:
Industrial: You can find them in robots, gas controllers, and surge protectors.
Medical: Rigid PCBs are important in machines like tomography and MRI systems.
Aerospace: They help with important tasks in airplane cockpit instruments and power converters.
Automotive: Rigid circuit boards are used in AC/DC converters and electronic control units (ECUs).
These uses show how important rigid circuit boards are in everyday technology. Their strong design helps them work well in tough conditions while keeping performance high.
Flexible Circuit Boards
Overview
Flexible circuit boards, also known as flexible PCBs, have special benefits compared to rigid circuit boards. They can bend, twist, and fold, which makes them great for tight spaces and light weights. Here are some important advantages of flexible circuit boards:
They offer wiring options that rigid boards cannot provide.
Their thin, light, and strong design allows for 3D packaging.
Flexible PCBs create less waste because they are thinner.
They last longer and are more durable, so replacements are needed less often.
These boards are easier to recycle and often use fewer harmful materials, making disposal safer.
Applications
Flexible circuit boards are used in many industries. Their flexibility makes them perfect for many devices. You can find them in:
Wearable Technology: Smartwatches and fitness trackers use flexible PCBs for their small designs.
Consumer Electronics: Smartphones and tablets use flexible circuits to save space and improve features.
Medical Devices: Tools like heart monitors and portable diagnostic devices benefit from the lightweight and strong nature of flexible PCBs.
Automotive Electronics: Flexible circuits are found in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and other small car parts.
The consumer electronics industry is the biggest user of flexible circuit boards. Manufacturers want to make smaller devices with better features. The rising need in wearable technology, car electronics, and healthcare pushes this trend. Flexible circuit boards are key in modern technology, allowing for new designs and better performance.
Feature | Rigid Circuit Boards | Flexible Circuit Boards |
|---|---|---|
Base Material | Non-conductive substrate with glass | Flexible base material like polyimide |
Conductive Material | Electro-deposited copper | Rolled annealed copper |
Manufacturing Process | Uses solder mask | Uses overlay or coverlay to protect circuitry |
Cost | Typically lower cost | Typically higher cost, but allows for compact designs |
Flexible circuit boards are very important in today’s technology world. Their ability to fit different shapes and sizes makes them valuable in many uses.
Rigid-Flex Circuit Boards
Overview
Rigid-flex circuit boards mix the best parts of rigid and flexible circuit boards. They have both hard and bendable parts, which allows for creative designs. The flexible parts run inside the rigid areas without any connection points. This design helps create smooth changes between the two types. This is important to avoid problems caused by stress.
When you design rigid-flex PCBs, follow these steps:
Turn on the Rigid-Flex mode in your design software.
Set up the Substack needed for each part of the board and align them.
Shape each rigid and flex area and assign the right Substack.
This mix of flexibility and strength makes these boards great for many uses.
Applications
You can find rigid-flex circuit boards in many modern electronic devices. Their special features make them good for different industries. Here are some common uses:
Medical Devices: Rigid-flex PCBs are key in pacemakers and cochlear implants, giving compact and reliable performance.
Military Equipment: These boards are important for weapon guidance systems and GPS tracking because they are tough.
Aerospace Systems: They support radar and control electronics, making them perfect for extreme conditions.
Telecommunications: Rigid-flex boards power 5G base stations and communication satellites, ensuring fast data transfer.
Automotive Systems: They run electronic control modules and infotainment displays, improving vehicle performance.
Industrial Applications: These boards support test equipment and automation systems, ensuring reliability in tough conditions.
Consumer Appliances: Rigid-flex PCBs allow for compact designs in devices like smart washing machines.
The flexibility of rigid-flex circuit boards lets you create new designs that meet the needs of today’s technology.
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Boards
Overview
High-Density Interconnect (HDI) boards are special circuit boards made for high performance. They have a compact design with many layers and thin lines. This setup allows for more connections in a smaller area. You can find HDI boards in many modern electronic devices because they are efficient and reliable.
Here are some important features of HDI boards:
Layer Count: HDI boards can have more layers than regular boards, usually between 4 to 20 layers.
Microvias: These boards use microvias, which are tiny holes that connect the layers. This helps save space and boost performance.
High Component Density: You can fit more parts on an HDI board, making them great for complex devices.
Applications
HDI boards are very important in many high-performance uses. Here are some common applications:
Smartphones: HDI boards help make smartphones compact, allowing for advanced features in a small size.
Tablets: These boards help tablets stay slim while offering strong processing power.
Medical Devices: In machines like MRI scanners and portable monitors, HDI boards ensure reliability and accuracy.
Aerospace: HDI technology is crucial in aerospace systems, where performance and strength are very important.
Automotive Electronics: Modern cars use HDI boards for advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and entertainment systems.
The flexibility of HDI boards makes them key in today’s tech world. Their ability to support complex designs while staying small helps engineers create new solutions in many fields.
LED Circuit Boards
Overview
LED circuit boards, also called LED PCBs, have special designs that make them different from other circuit boards. These boards need to handle heat well because LEDs produce heat when they work. Many LED PCBs use aluminum to manage heat better. This material helps spread out the heat, making sure the LEDs run well and last longer.
Here’s a comparison of what LED PCBs need versus other circuit boards:
Design Requirement | LED PCBs | Other PCBs |
|---|---|---|
Thermal Management | Needs good heat dissipation, often using aluminum for high power | Less important for low power applications |
Form Factor | Must fit rigid or flexible designs | Usually more standard |
Cost | Balances performance with cost | Often cheaper for standard types |
Environmental Conditions | Needs special materials for outdoor/high-temp areas | Less strict requirements |
Applications
LED circuit boards are used in many areas because they are efficient and last a long time. They are very important in lighting systems, where saving energy is key. LED modules use much less power than regular lights. They turn most energy into light, which cuts down waste and lowers electricity bills.
Here are some benefits of LED circuit boards:
Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
Energy Efficiency | LED modules use much less power and turn most energy into light, cutting down waste. |
Long Lifespan | They can last up to 50,000 hours or more, which means lower maintenance and replacement costs. |
Low Maintenance Costs | They need little maintenance because there are no moving parts, leading to lower service costs. |
You can find LED circuit boards in many products, such as:
Residential Lighting: LED bulbs and fixtures for homes.
Commercial Lighting: Energy-saving lighting solutions for offices and stores.
Automotive Lighting: Headlights, taillights, and interior lights in cars.
Display Screens: LED screens used in TVs and advertising displays.
The special features of LED circuit boards make them very important in today’s lighting solutions. Their ability to save energy and last a long time helps you save money and protect the environment.
Choosing the right type of circuit board is very important for your electronic projects. Each type, like single-sided or HDI boards, has its own purpose. Think about things like dielectric constant, thermal conductivity, and insertion loss when you choose. These factors affect how well your devices work and how reliable they are.
Making and throwing away printed circuit boards (PCBs) can harm the environment. This is because they use dangerous materials, create waste, and can pollute ecosystems. Using sustainable methods is important to reduce these problems.
By knowing these details, you can make smart choices that improve your designs while also caring for the environment.
FAQ
What is a circuit board?
A circuit board is a flat board that connects electronic parts. It lets electricity flow between these parts, helping devices work. You can find circuit boards in almost every electronic item, like smartphones and computers.
How do I choose the right circuit board type?
Think about how complex your project is, its size, and your budget. For simple devices, single-sided boards are good. For more complex uses, double-sided or multi-layer boards might be needed. Always check the specific needs of your design.
Can I make my own circuit board?
Yes, you can make your own circuit board! You can use software to design it and then etch it onto a board. Many online services also provide PCB manufacturing if you want a professional look.
What materials are used in circuit boards?
Common materials are fiberglass, epoxy resin, and copper. Fiberglass gives strength, while copper helps conduct electricity. The materials you choose affect how well the board works, how long it lasts, and its cost.
How do I recycle old circuit boards?
You can recycle old circuit boards by taking them to e-waste recycling centers. Many local electronics stores also have recycling programs. Proper recycling helps reduce harm to the environment and recover useful materials.
See Also
Understanding How PCBA Differs From Traditional PCB Designs
Essential Components of PCBA and Their Important Roles
An Overview of PCBA Applications in Everyday Electronics