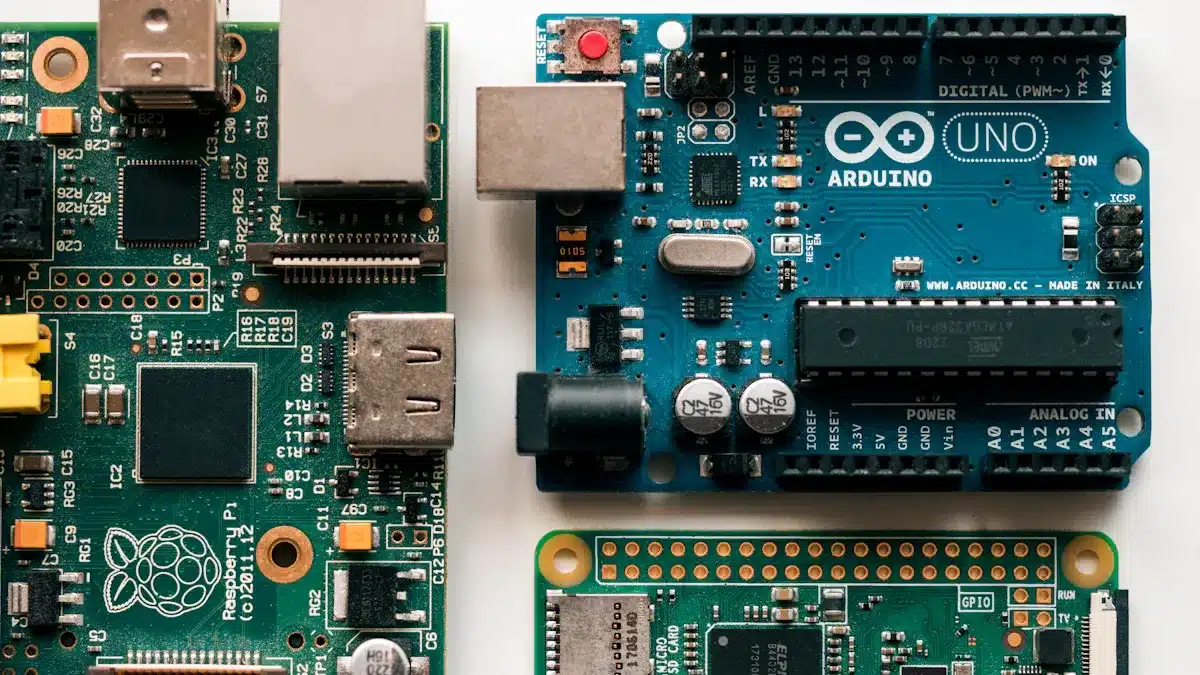
A circuit board board serves as the foundation in most electronic devices. Other electronic components are like the pieces placed on top of the circuit board board. You can think of a circuit board board like a city’s road map, connecting houses, shops, and schools. Each one represents a different electronic component. Understanding this difference helps people see how a circuit board board is unique. It provides structure and links all the parts, making it distinct from the components it supports.
Key Takeaways
Circuit boards are the main base in a device. They hold and connect all electronic parts. This makes them very important for the device to work.
There are different types of circuit boards. Some are single-sided, some are multilayer, and some are flexible. Each type is made for a special use or device need.
Electronic components like resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits do special electrical jobs. The circuit board only moves electricity between these parts.
A printed circuit board assembly (PCBA) is a circuit board with all its parts attached. It is ready to work in electronic devices.
Knowing how circuit boards and components are different helps you design, fix, and learn about electronics better and with more confidence.
Circuit Board Board Basics
Definition
A circuit board board acts as the main platform for connecting and supporting electronic parts. People often call it a pcb or printed circuit board. This board holds and links components like resistors, capacitors, and chips. Every circuit board board gives a device its structure and helps all the parts work together. Without a pcb, electronic devices would not have a way to organize or connect their parts.
Structure
A pcb has a layered design. Each layer serves a special purpose. The main materials and layers in a typical circuit board board include:
Substrate: This is usually made from FR-4 fiberglass. It gives the pcb strength and keeps electricity from leaking.
Copper foil layers: These thin sheets of copper form the paths for electricity to flow. Some pcbs have copper on one side, others on both, and some have many layers.
Prepreg resin: This sticky layer bonds the copper and core layers in multi-layer pcbs.
Solder mask: This colored layer, often green, covers the copper tracks. It protects them and stops solder from spreading.
Silkscreen: This white ink layer prints labels and symbols on the pcb surface.
Some circuit board boards use different materials. For example, flexible pcbs use bendable plastic, and metal-cored boards use aluminum for better heat control.
Function
The main job of a circuit board board is to connect electronic components and let electricity flow between them. The pcb acts like a map, guiding signals to the right places. It also holds the parts in place so they do not move or touch each other by mistake. In every electronic device, the circuit board board makes sure all the parts work as a team. Without the pcb, the device would not function as planned.
Printed Circuit Board and PCB Types
PCB vs. PCBA
A pcb is a flat board that connects electronic parts. It has copper tracks for electricity to move. When all the parts are put on, it becomes a printed circuit board assembly. People call this a pcba. The main difference is easy to see. A pcb is empty, but a pcba has all the needed parts. Engineers say pcba when they mean a finished board. A pcb alone cannot work until it is a pcba. In factories, workers or machines add resistors and chips to make a pcba. Every electronic device uses a pcba, not just a plain pcb.
PWB and Modern PCB
Long ago, people used the word printed wiring board, or PWB. These boards had only wires and no parts. Today, most people say printed circuit board instead. Both words mean almost the same thing. A modern pcb has copper paths on a strong base. It holds and connects all the parts in a device. The biggest difference between PWB and pcb is the name. Now, most people use pcb for all boards. The way a pcb is made and used is mostly the same. Only the name has changed over time.
Motherboards
Motherboards are special pcbs. They are the main part in computers and smart devices. A motherboard connects the CPU, memory, storage, and other parts. It has many slots, sockets, and ports. This makes it more complex than other pcbs. Motherboards have heat sinks and fans to stay cool. You can upgrade them by adding more RAM or a new graphics card. Other pcbs in devices are smaller and simpler. Motherboards help all computer parts work together.
Tip: There are many types of pcbs. These include single-sided, double-sided, multilayer circuit board, flexible pcbs, rigid-flex, and high-density interconnect boards. Each type is used for different jobs in electronics.
PCB Type | Layer Count | Substrate Type | Key Characteristics | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Single-Sided | 1 | Rigid (e.g., FR-4) | Conductive traces on one side; simple and low cost | Simple devices, prototyping, educational use |
Double-Sided | 2 | Rigid | Conductive traces on both sides; moderate complexity | Consumer electronics |
Multi-Layer | 3 or more | Rigid | Multiple conductive layers; high complexity and density | High-performance systems, aerospace, RF |
Flexible | 1 or more | Flexible (polyimide, polyester) | Bendable, lightweight, space-saving | Wearables, compact electronics, automotive |
Rigid-Flex | Combination of rigid and flexible | Mixed (rigid + flexible) | Integrated rigid and flexible sections; 3D packaging | Aerospace, medical devices, automotive |
Multi-layer with fine pitch | Rigid or rigid-flex | Fine traces, microvias, high component density | Smartphones, high-performance computing, wearables, medical devices |
The type of pcb depends on the number of layers and the materials. Some devices need a simple pcb. Others use a multilayer circuit board for harder jobs. Flexible pcbs help save space in small gadgets. Each pcba uses the right pcb for its job.
Other Electronic Components
Passive Components
Passive components do not need power to work. They cannot add energy to a circuit. They only control how electricity moves. Some common passive components are resistors, capacitors, and inductors. A resistor slows down the current in a circuit. A capacitor can hold and release electrical energy. An inductor stops quick changes in current. These parts help shape signals and keep other parts safe. You can find them in almost every device, like radios and computers.
Active Components
Active components use energy to control electricity. They can make signals stronger or turn them on and off. Transistors and diodes are two main active components. A transistor can be a switch or an amplifier. It helps control how circuits work. A diode lets current go in just one direction. Active components are very important in digital electronics.
Integrated Circuits
An integrated circuit puts many small electronic parts into one chip. This chip can do hard jobs, like handling data or saving information. Engineers use integrated circuits in almost every new device. These circuits save space and make devices work better.
There are different ways to put an integrated circuit on a circuit board. Some use through-hole mounting, where pins go through holes in the board. Others use surface-mount technology, which puts the chip right on top of the board. Surface-mount technology helps make smaller and faster devices.
Mounting Type | Description | Typical Package Examples | Mounting Method Details |
|---|---|---|---|
Through-Hole | Larger packages with pins inserted through holes in the PCB and soldered on the opposite side. | DIP (Dual In-line Package) | Pins go through PCB holes; can be soldered directly or inserted into sockets for easy replacement. |
Surface-Mount | Smaller packages soldered directly onto the PCB surface. | SOIC, SSOP, QFP, QFN, BGA | Pins arranged around edges or in a matrix underneath; require specially designed PCBs and soldering tools. |
Integrated circuits help make modern electronics possible. They let engineers build strong computers, phones, and many other devices.
Key Differences
Physical Structure
A pcb looks like a flat, thin board. It often has a green surface with copper lines running across it. These lines form paths for electricity. The pcb uses layers of fiberglass, copper, and resin. Each layer has a job. The top layer holds the copper tracks. The middle layer gives strength. The bottom layer protects the board. A printed circuit board can be rigid or flexible. Some devices need a flexible pcb to fit into small spaces.
Other electronic components have different shapes and sizes. A resistor looks like a small tube with colored bands. A capacitor can look like a tiny can or a flat disc. An integrated circuit often looks like a black rectangle with metal legs. These parts do not have layers like a pcb. They sit on top of the pcb or pcba. The pcb gives them a place to stay and connects them together.
A pcba shows a big change in structure. It is a pcb with all the electronic components attached. The pcba looks busy, with many parts on its surface. Each part has a special spot. The pcba holds everything in place and keeps the parts from moving.
Note: The key differences in physical structure help people see how a pcb or pcba forms the base, while each component adds a special function.
Electrical Function
The pcb acts like a road system for electricity. It does not change the signal or store energy. It only guides the flow from one part to another. The copper tracks on the pcb make sure signals reach the right places. The printed circuit board does not work alone. It needs electronic components to do real jobs.
Electronic components handle the main electrical tasks. A resistor slows down the current. A capacitor stores and releases energy. An integrated circuit can process data or control signals. Each component has a job that changes or controls electricity. The pcb only connects these parts.
A pcba brings everything together. It lets the electronic components work as a team. The pcba makes sure each signal goes to the right part. The integrated circuit on a pcba can run a computer or control a robot. The pcba does not change the signal by itself. It lets the parts do their work.
Role | PCB/PCBA | Electronic Components |
|---|---|---|
Main Function | Connects and supports parts | Performs electrical tasks |
Signal Handling | Guides signals | Changes, stores, or controls signals |
Example | Motherboard, phone main board | Resistor, capacitor, integrated circuit |
Integration and Assembly
The pcb gives a home to all electronic components. It has holes and pads for each part. During assembly, workers or machines place each component on the pcb. When all parts are in place, the board becomes a pcba. The pcba is ready to use in a device.
The key differences in integration show up during assembly. The pcb starts empty. The pcba is full of parts. The process of turning a pcb into a pcba is called assembly. This step joins the electronic components to the board. The integrated circuit often goes on the pcba last because it is sensitive.
A pcba can hold many types of parts. It can have resistors, capacitors, and more than one integrated circuit. The pcba makes sure all parts work together. Without the pcb, the parts would not connect. Without the electronic components, the pcb would do nothing.
🛠️ Tip: When building or fixing devices, people check the pcba first. They look for missing or broken parts. The pcba shows how all the parts fit and work together.
Why Differences Matter
Design and Manufacturing
Designers and engineers need to know how a pcb is different from other electronic parts. The pcb is the main base for all the parts. Every pcba starts as a plain pcb. In factories, workers or machines put resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits on the board. They use special tools like pick-and-place machines and soldering stations. Surface-mount technology makes this job quicker and more exact. Different jobs need different kinds of pcbs. A simple toy might use a single-layer pcb. A smartphone needs a complex multilayer board. The type of pcb changes the cost, size, and how well the device works. Good pcb making helps the final pcba work right in its job.
Repair and Troubleshooting
Repair workers usually look at the pcba first. They search for broken or missing parts. If something stops working, it could be a bad pcb or a broken part on the pcba. Knowing the difference helps them fix things faster. A cracked pcb can break the link between parts. A bad resistor or chip on the pcba can stop the device. Fast and correct repairs keep things running in many places. Knowing how the pcb and parts work together makes fixing problems easier.
Learning Electronics
Students and beginners learn better when they see how a pcb and its parts work together. Books like ‘A Person-Centered Guide to Demystifying Technology’ give clear examples. These books show the difference between drawings and real boards. They use breadboards and pcbs to help students build easy circuits. Simple steps, like lighting an LED with a resistor, make ideas easy to get. Resources like the Adafruit Learning System and science rules give more help and examples. By using real pcba examples, students see how parts fit and work together in real life.
Circuit boards are special because they hold and link all the parts in a device. Other components do one job, but the circuit board is the base for everything. Knowing this helps people pick the right board, fix things, and plan projects.
Find out which PCB type fits your project best.
Test and check your work to get better results.
Use the right rules to make your work strong and safe.
When you know these differences, you can learn and work with electronics with more confidence.
FAQ
What is the main job of a circuit board?
A circuit board connects and supports all electronic parts in a device. It acts as a base and provides paths for electricity to flow between components.
How does a PCB differ from an integrated circuit?
A PCB is a board that links and holds parts. An integrated circuit is a small chip that performs specific tasks. The PCB connects many components, including integrated circuits.
Can someone repair a PCB at home?
Yes, people can repair simple PCBs at home. They need basic tools like a soldering iron and replacement parts. Complex boards may require special equipment.
Why do some circuit boards bend while others stay rigid?
Flexible circuit boards use bendable materials like plastic. Rigid boards use strong materials like fiberglass. The choice depends on the device’s needs.
What happens if a component is missing from a PCBA?
If a component is missing, the device may not work correctly. Each part has a job. Missing parts can stop signals or cause errors.
See Also
Understanding How PCBA And PCB Differ In Structure And Function
The Importance And Operation Of PCBA Motherboards Explained
Unveiling Key Distinctions Between PCBA And PCB Components