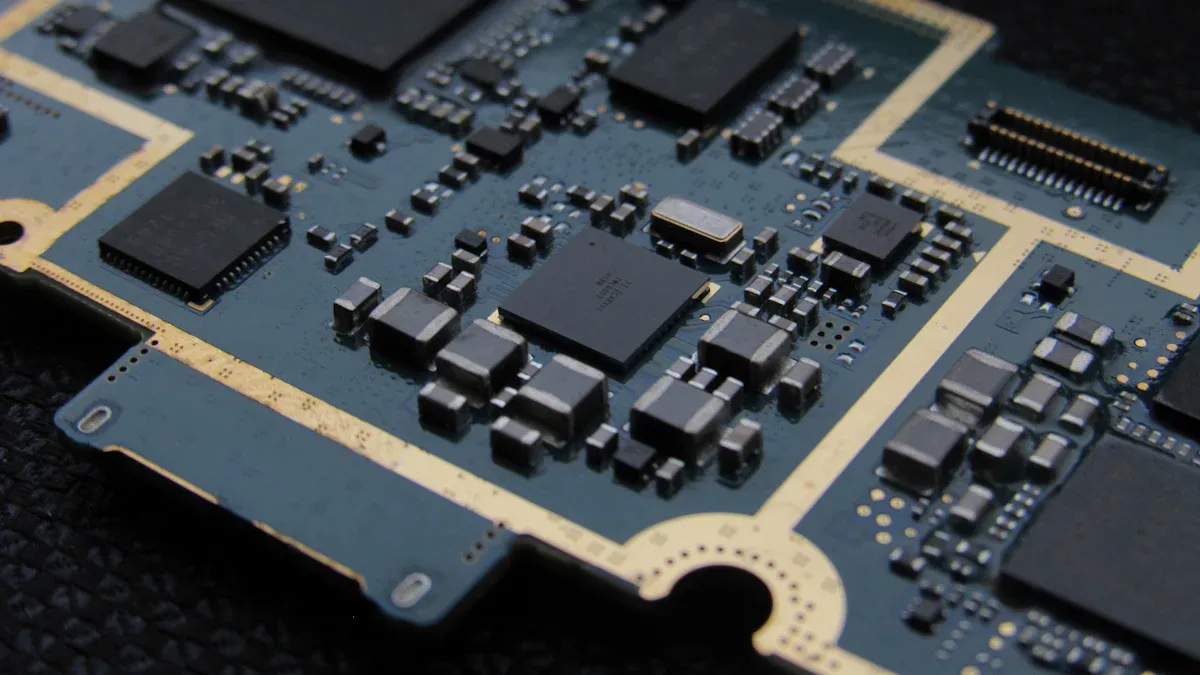
A PCBA motherboard is the main part of your device. It helps parts like the processor, memory, and storage work together. This teamwork makes your device run well and handle modern tasks. New designs have made motherboards much better. For example:
Devices now start in about 40 seconds, saving time.
Data moves faster, so you can finish tasks quickly.
Better heat and shake resistance make them last longer.
Knowing about PCBA motherboards helps you choose wisely. It makes sure your device parts work well and stay reliable.
Key Takeaways
A PCBA motherboard links all parts of your device. It helps them work together properly for good performance.
When picking a motherboard, make sure it fits your CPU and RAM. This prevents problems and keeps your device running smoothly.
Choose motherboards with strong power systems and good cooling. These features boost performance and make your device last longer.
Check how many and what kind of ports the motherboard has. This lets you connect devices easily and upgrade later if needed.
Think about cost and future upgrades when buying a motherboard. Pick one that works for now but can improve later.
What is a PCBA Motherboard?
Definition and Difference from a PCB
A PCBA motherboard is a circuit board with all its parts attached. It connects and controls parts like the processor, memory, and storage. A PCB is just the empty board with circuits on it. A PCBA motherboard has all the needed parts soldered on, ready to work in devices.
Think of a PCB as the frame of a device. The PCBA motherboard is the working machine. To make it, parts like resistors and chipsets are placed and soldered onto the board. This step lets the motherboard do its job. If you’ve wondered how to solder or place PCB parts, these steps are key for building a strong PCBA motherboard.
Role in Electronic Devices
The PCBA motherboard helps your device run smoothly. It lets all the parts talk to each other and work together. Without it, your device couldn’t store data, process tasks, or even turn on.
PCBA motherboards are used in many areas. In factories, they control robots and conveyor belts. Medical tools like MRI machines need them for accuracy. In airplanes, they manage cockpit controls and sensors. Even cars use them for dashboards and power systems. These examples show how important PCBA motherboards are for today’s technology.
Knowing how to pick PCB parts and fix broken ones can help your device last longer. A good PCBA motherboard is strong, works well, and fits with other parts. It’s a key part of electronic devices.
Key Parts of a PCBA Motherboard
The motherboard is the heart of any device. It holds important parts that work together to make your device run well. Let’s look at these parts and what they do.
Microprocessor and Chipsets
The microprocessor, or CPU, is like the brain. It does all the thinking and calculations for your device. Without it, your device won’t work. The chipset is like a traffic controller. It helps the CPU, memory, and other parts share data smoothly. Together, they decide how fast your device works and handles tough tasks.
For example, the chipset helps the CPU talk to storage and graphics cards. This teamwork makes your device faster and more stable. A good chipset also allows quicker data transfers, improving performance.
Tip: When buying a motherboard, check if the CPU and chipset match. This makes it easier to upgrade later without replacing the whole board.
Memory Modules
Memory modules, or RAM, store data temporarily while your device is on. They help the CPU get information quickly, speeding up tasks like opening apps or browsing. More RAM means better multitasking for your device.
Modern motherboards support faster RAM, which helps with gaming or video editing. For example, DDR4 or DDR5 RAM slots allow quicker data movement. This keeps your device running smoothly, even with big files or many programs open.
Note: Check how much RAM your motherboard can handle. This helps you avoid problems and get the best performance.
Power Supply and Regulators
The power supply and regulators give steady power to all parts. They make sure each part gets the right amount of electricity. Regulators stop power spikes that could harm the CPU or memory.
A good power system has strong voltage control and layers for power flow. This keeps your device working well, even during heavy use. Heat sinks and fans help keep the motherboard cool. This protects parts and makes them last longer.
Part Type | Why It’s Important | Features That Help |
|---|---|---|
Power Flow | Gives steady power and reduces electrical problems | Uses strong voltage control and layered power systems |
Cooling System | Keeps parts cool for better performance | Includes heat sinks and fan spots for cooling |
Active Parts | Controls power and signals in circuits | Has diodes, transistors, and advanced chips |
Passive Parts | Helps active parts and manages signals | Includes resistors, capacitors, and inductors |
Tip: Choose motherboards with good power systems. They save energy and improve how your device works.
Input/Output Ports
Input/Output (I/O) ports connect your motherboard to other devices. These ports let you use keyboards, mice, monitors, and storage drives. Without them, your computer couldn’t work with external devices.
Modern motherboards have many I/O ports for different uses. Common ones are USB, HDMI, Ethernet, and audio jacks. USB ports are useful for file transfers and connecting gadgets. HDMI ports link monitors or TVs for clear video. Ethernet ports give stable internet, and audio jacks handle sound for headphones or speakers.
Some motherboards also have special ports like Thunderbolt for faster data or DisplayPort for better video. The ports are placed carefully on the board for easy use and strong signals. For example, USB ports are grouped together, and audio jacks are near the edge for quick access.
Tip: Check the number and type of I/O ports before buying a motherboard. This helps ensure it works with your devices and allows upgrades later.
Other Important Parts
Motherboards also have smaller parts that are very important. These parts help the motherboard work well and stay safe from damage.
Passive Parts
Passive parts include resistors, capacitors, and inductors. Resistors control electricity flow, capacitors store and release energy, and inductors reduce noise. Together, they keep signals steady and prevent problems.
Active Parts
Active parts like transistors and diodes manage power and signals. Transistors act like switches, controlling electricity flow. Diodes make sure electricity flows one way, protecting the board from power surges. These parts are placed carefully for the best performance.
Heat Control Parts
Heat sinks and fans stop the motherboard from overheating. Heat sinks pull heat away from the CPU and chipset. Fans push the heat out. Good heat control keeps parts working longer and better during heavy use.
Connectors and Slots
Connectors and slots let you add new features to your motherboard. PCIe slots hold graphics cards, and SATA connectors link storage drives. These parts make it easy to upgrade your motherboard.
Note: A good motherboard balances all these parts for strong performance. Look at the layout and cooling features when choosing one.
How a PCBA Motherboard Works

Data Flow Through the Motherboard
The motherboard is the main center for moving data. It links the CPU, memory, storage, and other parts to work together. When you open an app or save something, the CPU handles the data. Then, it sends it to memory or storage. The chipset helps guide this process, making sure data goes to the right place.
Data moves through tiny paths called traces on the board. These paths are designed to avoid problems and keep speeds high. For example, fast traces connect the CPU to RAM for quick data access. The way these paths are arranged affects how well the motherboard works.
Tip: A good PCB motherboard moves data faster and avoids errors. This makes your device work better overall.
Power Distribution and Regulation
The motherboard also spreads power to all its parts. It makes sure each part gets the right amount of electricity. Regulators stop power spikes that could harm the CPU or memory. For instance, voltage regulators keep power steady, even when the device is working hard.
The power system is built with layers to help power flow smoothly. Heat sinks and fans keep the board cool by managing heat. This stops overheating and helps the parts last longer.
Note: Picking a motherboard with strong power control makes it more reliable and keeps it running well.
Component Interaction for Functionality
How parts work together decides how well the motherboard performs. Each part, like the CPU and chipset, has a job. For example, the CPU processes tasks, and the chipset helps move data between memory and storage.
Good soldering keeps parts firmly attached to the board. Methods like surface mounting and wave-soldering stop problems caused by heat or movement. Managing heat is also important. Parts like capacitors need protection from too much heat to avoid damage or fire risks.
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Weak designs or heavy loads can break fragile parts like ceramic capacitors. | |
Soldering techniques | Using proper soldering methods, like surface mounting, prevents issues from heat or movement. |
Thermal management | Protecting parts like capacitors from heat stress avoids damage or fire risks. |
Tip: A well-made motherboard with strong soldering and design helps parts work smoothly together, improving performance.
Why Technical Specifications Matter
Technical specifications are the key to a good PCB motherboard. They decide how well it works, fits with other parts, and lasts. Knowing these details helps you pick or upgrade your device wisely.
Optimizing Motherboard Performance
A motherboard’s performance depends on its technical specifications. These specs show if it can handle tough tasks like gaming or editing. For example, server motherboards are built for high-performance jobs. They can use over 1TB of RAM, perfect for data centers. They also have multiple LAN ports for strong network connections.
Some motherboards are made for specific tasks, like running websites or databases. These are great for heavy loads and staying online. Desktop motherboards are for gaming or creating content. Picking the right motherboard for your needs is very important.
Tip: For high-performance tasks, choose motherboards with ECC RAM support. This helps find errors and keeps your system stable for big jobs.
Ensuring Hardware Compatibility
Technical specifications help make sure your motherboard works with other parts. A good PCB motherboard supports fast bus speeds, like 100 MHz. To do this, makers focus on timing, layout, and signal quality. For example, timing must be shared well between the CPU, chipset, and memory.
The PCB’s design, like trace size and material, affects how signals move. These details help the motherboard connect with parts like the CPU and RAM. Without good compatibility, your device might not work right or fail completely.
Note: Always check if a motherboard supports your CPU, RAM, and other parts. This avoids problems and saves money on fixes or upgrades.
Enhancing Reliability and Longevity
A reliable motherboard lasts longer and works better. Gaming PCs need strong motherboards for heavy use. New designs, like the PC Endurance Board, are made to handle tough tasks and stay durable.
Reliability depends on managing heat, power, and signals well. Features like heat sinks, voltage regulators, and good capacitors make motherboards stronger. A well-made PCB also keeps parts safe and firmly in place.
Tip: Choose motherboards with good cooling and power systems. These features improve performance and help your device last longer.
Balancing Cost and Upgradability
Picking a PCBA motherboard needs a balance of cost and upgrades. Spending too much on unneeded features wastes money. But buying one with few upgrade options limits future performance. Knowing how to balance these helps you choose wisely.
Why Cost Matters
The price shows the features and quality of a motherboard. Expensive ones have faster RAM slots, more PCIe lanes, and better cooling. These improve performance but cost more. If you don’t need extras, mid-range boards save money and work well.
Tip: List the features you need now. Don’t pay for extras you won’t use.
Why Upgradability Matters
Technology changes fast. A motherboard with upgrade options keeps your device useful longer. Extra RAM slots, PCIe lanes, and newer CPU support help your device stay updated.
For example, DDR5 RAM support allows faster memory upgrades. Multiple SATA connectors let you add storage drives. These features save money by extending your device’s life.
How to Balance Cost and Upgradability
Follow these steps to find the right balance:
Set a Budget: Decide your spending limit. Stick to it to avoid overspending.
Prioritize Features: Pick features that match your tasks. Gamers need strong graphics support. Office users need good RAM capacity and speed.
Check Compatibility: Make sure the motherboard supports future upgrades. Look at CPU sockets, RAM slots, and expansion ports.
Compare Options: Research models in your budget. Compare their features and upgrade potential.
Example Comparison Table
Feature | Budget-Friendly Option | Upgrade-Friendly Option |
|---|---|---|
RAM Support | DDR4, up to 32GB | DDR5, up to 128GB |
PCIe Slots | 1 PCIe x16 slot | 2 PCIe x16 slots |
Storage Connectors | 2 SATA ports | 4 SATA ports + NVMe support |
Cooling System | Basic heat sink | Advanced heat sink + fan slots |
Note: Pick a motherboard that fits your needs now but allows upgrades. This gives you the best value for your money.
Final Thoughts
Balancing cost and upgrades takes planning. Focus on key features and future-proofing your device. This avoids overspending and ensures long-term performance. Research and compare options carefully. This way, you build a system for today and tomorrow.
Common Technical Specifications of a PCBA Motherboard
Form Factor and Dimensions
The form factor decides the size and shape of the motherboard. It also affects how many parts it can hold. Common types are ATX, Micro ATX, and Mini-ITX. Each has different sizes and features. For example:
Form Factor | Dimensions | Expansion Slots | DIMM Slots |
|---|---|---|---|
ATX | 12” × 9.6” | 7 | 4 |
Micro ATX | 9.6” × 9.6” | 2 | 4 |
Mini-ITX | 6.7” × 6.7” | 1 | 2 |
If you need more slots for upgrades, ATX or Micro ATX is better. Mini-ITX is great for small devices but has fewer slots.
Tip: Make sure your case size and cooling system match the form factor.
Socket Type and Chipset
The socket type connects the CPU to the motherboard. It must match your CPU to work properly. Common socket types are LGA, PGA, and BGA. For example, Intel uses LGA, while AMD often uses PGA.
The chipset is like the motherboard’s manager. It helps the CPU, RAM, and other parts work together. High-end chipsets allow faster data and extra features like overclocking.
Note: Choosing the right socket type and chipset ensures your device works well.
RAM Capacity and Speed
RAM size and speed affect how well your device multitasks. Modern motherboards support DDR4 or DDR5 RAM, with speeds from 2400 MHz to over 6000 MHz.
More RAM slots let you add memory later. For example, ATX boards usually have four slots, while Mini-ITX boards have two. Faster RAM helps with gaming and editing tasks.
Tip: Check your motherboard’s RAM limits and speeds to avoid slowdowns.
Expansion Slots and Ports
Expansion slots and ports let you add new parts to your motherboard. These slots connect things like graphics cards, sound cards, or Wi-Fi adapters. They make your device stronger and more flexible for different tasks.
The PCIe slot is the most common type. It comes in sizes like x1, x4, x8, and x16. Bigger sizes handle more data. For example, PCIe x16 is great for powerful graphics cards. Smaller ones, like PCIe x1, are good for sound cards or network adapters.
Motherboards also have ports for outside devices. USB ports connect keyboards, mice, and storage drives. HDMI and DisplayPort send video to monitors. Ethernet ports give steady internet. Some boards even have Thunderbolt ports for faster data.
When picking a motherboard, check its slots and ports. Make sure it fits your needs now and allows upgrades later. For example, if you want two graphics cards, choose a board with extra PCIe x16 slots.
Tip: Match the slots and ports to your parts. This avoids problems and keeps your device working well.
Power Requirements and Standards
The motherboard’s power system is very important. It sends electricity to all parts, helping them work properly. Voltage regulators control power flow and protect parts like the CPU and memory.
Motherboards follow rules like ATX standards. These rules decide the size, shape, and power connectors. For example, ATX boards use 24-pin connectors. Smaller boards, like Mini-ITX, use fewer pins.
Power needs depend on the parts you add. Strong parts, like gaming GPUs, need more power. A good power supply unit (PSU) gives enough electricity and stops power surges. This keeps the motherboard safe.
When choosing a motherboard, think about its power needs and PSU compatibility. Look for features like good voltage control and heat management. These help your device last longer and work better.
Note: A strong power system improves performance and protects your motherboard from damage.
A PCBA motherboard is very important in today’s devices. It helps all parts work together and keeps performance steady. Knowing its features helps you pick or upgrade hardware wisely. This knowledge makes your device work better and last longer.
Electronics are growing fast, increasing the need for good motherboards. New designs, like extra layers, improve signals and power flow. These changes make devices work better in many fields.
Use what you’ve learned to choose the best motherboard. This keeps your device running well and ready for the future.
FAQ
What is the difference between a PCBA and a PCB?
A PCB is just a plain board with circuits. A PCBA has all its parts attached and ready to work. Think of a PCB as an empty page and a PCBA as a finished book.
How do I know if a motherboard is compatible with my CPU?
Look at the socket type and chipset on the motherboard. These must match your CPU. For example, Intel CPUs use LGA sockets, while AMD CPUs often use PGA sockets. Always check the motherboard’s details before buying.
Why does the form factor of a motherboard matter?
The form factor decides the size and features of the motherboard. ATX boards have more slots for upgrades. Mini-ITX boards are smaller but hold fewer parts. Pick one that fits your case and future needs.
Can I upgrade my motherboard later?
Yes, but it depends on your device’s setup. Make sure the new motherboard fits your case. Also, check if your CPU and RAM will work with it. You might need to reinstall your operating system after upgrading.
What features should I prioritize when buying a motherboard?
Focus on parts that match your needs. Look for enough RAM slots, PCIe lanes, and storage connectors. A good cooling system and steady power supply help it last longer. Choose features based on what you’ll use it for, like gaming or office tasks.
Tip: Compare different models to find the best one for your budget and needs.
See Also
Understanding PCBA: Definition and Its Importance in Electronics
The Importance of PCB Design in Modern Electronic Devices
Exploring PCBA: Definition and Its Significance in Electronics
Defining PCBA and Its Essential Function in Electronics
PCBA Explained: Definition and Major Applications in Electronics