The printed circuit board (PCB) industry is very important in today’s electronics. The global market size is expected to reach $155.38 billion by 2037. This means the need for PCBs is growing. More people are using Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Also, 5G networks are being set up. These changes show why we must understand both pcb manufacturing and assembly. As technology changes, we need better and faster PCBs. They are needed for many uses, like consumer electronics and electric cars.
Key Takeaways
PCB manufacturing makes the empty circuit boards. PCB assembly puts electronic parts on them to make them work.
Quality control is very important in both steps. It helps ensure reliability and meets industry standards.
Knowing how long each process takes helps plan production schedules better.
Picking the right materials affects how well PCBs work and their cost. So, choose wisely.
Staying updated with trends like automation and eco-friendly practices can improve production efficiency.
PCB Manufacturing Overview

PCB manufacturing is the process of making printed circuit boards (PCBs). These boards are very important for electronic devices. This process is key because it affects how good and reliable the final product is. High-quality PCBs help electronic devices work well and efficiently.
Key Processes in PCB Fabrication
The PCB fabrication process has several important steps. Each step is necessary to make a working PCB. The main steps are:
Design and Prototyping: Engineers use PCB design software to make layouts and prototypes. This stage lets them make changes before starting production.
Material Selection: Manufacturers pick the right base materials, like FR4 or Rogers, based on what the PCB needs.
PCB Fabrication: This step includes printing circuit designs, etching, drilling, and adding surface finishes. Automated machines usually do these tasks to ensure accuracy.
Layering for Multi-layer PCBs: For complex designs, manufacturers stack and laminate several layers, drilling them as needed.
Quality Assurance: Visual checks and advanced tests, like X-ray inspections, make sure the PCBs meet quality standards.
Assembly: Components are put on the PCB and soldered tightly. This step is very important for the final product to work.
Packaging and Shipping: After cleaning, the PCBs are packaged and readied for delivery to customers.
These processes help manufacturers create high-quality PCBs that meet the growing need for reliable electronic devices.
Importance of PCB Manufacturing
PCB manufacturing greatly affects how well electronic devices work. Good manufacturing methods improve signal quality and speed. This allows electrical signals to move without problems. Good thermal management during manufacturing stops overheating, which can help devices last longer. Also, placing components accurately reduces mistakes that could cause issues.
Additionally, the materials used in PCB manufacturing influence the overall quality. For example, FR4 is a popular material because it is strong and stable at high temperatures. Other materials, like Rogers, provide better electrical performance for fast applications.
Environmental factors also matter in PCB manufacturing. Manufacturers must follow rules like RoHS and REACH, which limit harmful substances and encourage responsible waste management. By using eco-friendly methods, manufacturers can lessen their environmental impact while meeting the rising demand for PCBs.
PCB Assembly Process
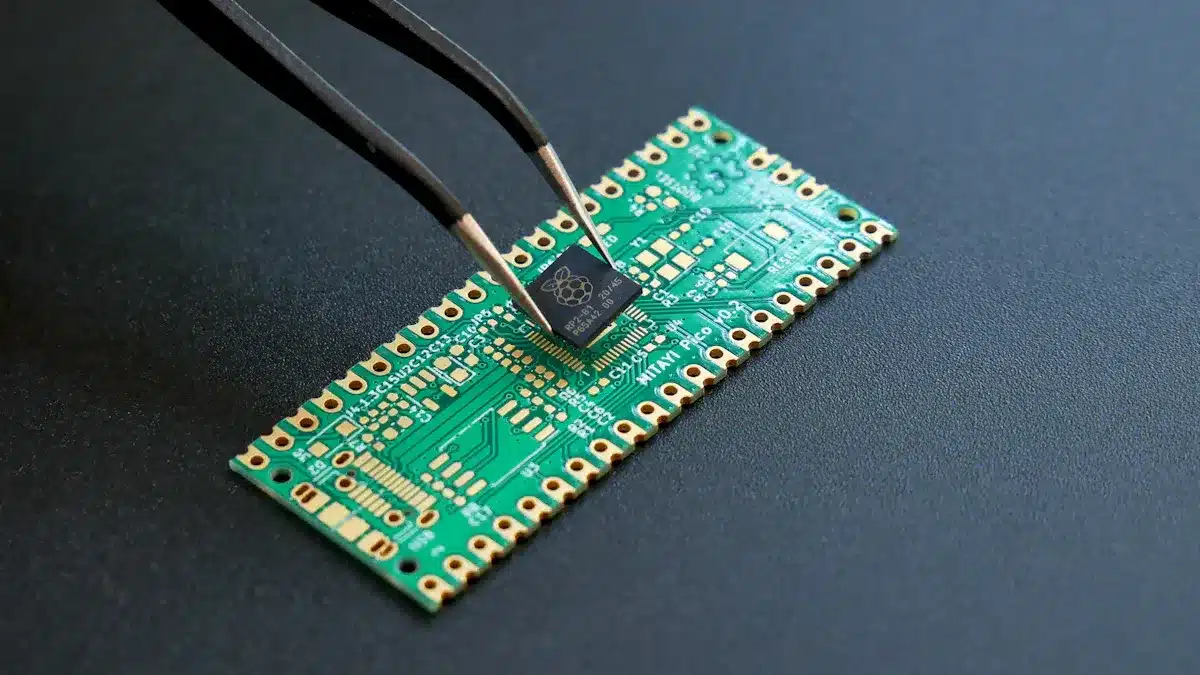
PCB assembly is when electronic parts are put on a printed circuit board (PCB). These parts are connected to make a working electronic device. This process is very important in electronics. It changes a bare PCB into a complete product. The assembly process makes sure all parts work well together. This helps the overall function of electronic devices.
Steps in PCB Assembly
The PCB assembly process has several steps. Each step is important for making sure the final product is good and reliable. Here are the main steps involved:
Design and Preparation: Finish the PCB design, make the schematic and layout, and create manufacturing files.
Stencil Printing (Solder Paste Application): Use a stencil to put solder paste on the PCB for surface mount technology (SMT).
Component Placement: Use machines to place components on the PCB for SMT or do it by hand for through-hole parts.
Reflow Soldering (For SMT): Heat the PCB in a reflow oven to melt solder paste and make connections.
Wave Soldering (For Through-Hole): Use wave soldering for through-hole parts to attach them to the PCB.
Inspection and Testing: Check the work using Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and do functional tests.
Final Assembly and Packaging: Put the PCB into a larger system and package it for shipping.
These steps help make the assembly process smooth and ensure the final product is high quality.
Importance of PCB Assembly
PCB assembly is very important for how electronic products work. Here are some key points about its importance:
Aspect | Contribution to Functionality |
|---|---|
Product Reliability | Makes sure only perfect products reach the market through careful checks and tests. |
Customer Satisfaction | Good assemblies lead to reliable performance and longer life, improving user experience. |
Compliance with Standards | Following industry rules builds trust and keeps product quality high. |
Risk Mitigation | Reduces the chance of faulty products, protecting manufacturers from problems and bad reviews. |
The assembly process also has challenges. For example, creating good PCB test procedures takes a lot of time and skill. It can be hard to balance thorough testing with speed and costs. Also, placing parts correctly is very important because parts are getting smaller. Small mistakes can cause big problems like electrical short circuits.
Modern PCB assembly lines use important machines to improve speed and accuracy. Some of these include:
Wave Soldering Machines: Automate the soldering process using a wave of hot solder.
Pick and Place Machines: Quickly and accurately place parts on the board.
Reflow Ovens: Heat assembled PCBs to melt solder paste for connections.
Soldering Equipment: Connect parts to a PCB using different soldering tools.
Comparing PCB Manufacturing and Assembly
Timeframes and Costs
PCB manufacturing and assembly are different when it comes to time and costs. Making a PCB usually takes 3 to 14 days. In contrast, putting together a PCB takes about 1 to 5 days. This difference is due to how complicated the manufacturing steps are.
Here’s a simple look at the average time for each process:
Process | Average Timeframe |
|---|---|
PCB Manufacturing | 3 to 14 days |
PCB Assembly | 1 to 5 days |
Many things affect the costs of PCB manufacturing and assembly. Here are some key points to think about:
Material Costs: The type of base material and copper thickness can change costs.
Process Costs: More layers and complicated steps can raise expenses.
Quantity & Batch Effects: Making more items can lower the cost per unit.
Also, urgent orders can make labor and shipping costs go up. More complex circuits need more parts, which raises costs. Bigger boards cost more for materials and shipping. More layers also add to material and manufacturing costs.
Quality Control in PCB Processes
Quality control is very important in both PCB manufacturing and assembly. Each process has its own focus to make sure the final product meets industry standards.
Process | Quality Control Focus |
|---|---|
PCB Manufacturing | Makes sure design requirements are met through different testing methods. |
PCB Assembly | Focuses on checking and testing assembled boards to ensure parts are placed and soldered correctly. |
In PCB manufacturing, quality control includes:
Checking raw materials
Inspections during different production stages
Final tests of completed PCBs
On the other hand, quality control in PCB assembly focuses on:
Checking the assembled board
Testing to make sure all parts are in the right place and soldered
Verifying that the final product works correctly
Quality control is very important. It helps cut down on mistakes and failures during production. This ensures reliable products that meet what customers expect.
Knowing the differences between PCB manufacturing and assembly is very important for anyone working in electronics. Both steps are key to making reliable devices.
In the future, some trends will change the industry:
AI and Automation: These tools will make things faster and improve quality checks.
Miniaturization: Smaller gadgets will increase the need for High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs.
Eco-Friendly Practices: Green manufacturing will be more important.
Companies can get better results by making designs simpler, choosing the right materials, and encouraging teamwork early on. These methods will help create better products and make operations run smoother.
By keeping up with these trends and methods, manufacturers can make sure they meet the changing needs of the electronics market.
FAQ
What is the main difference between PCB manufacturing and assembly?
PCB manufacturing makes the empty circuit boards. PCB assembly puts and solders electronic parts onto those boards.
How long does PCB manufacturing typically take?
PCB manufacturing usually takes 3 to 14 days. This depends on how complex the design is.
Why is quality control important in PCB processes?
Quality control makes sure that both manufacturing and assembly follow industry rules. It helps stop mistakes and ensures devices work well.
What materials are commonly used in PCB manufacturing?
Common materials are FR4, which is a fiberglass epoxy, and Rogers, which gives better electrical performance for fast applications.
How can companies reduce costs in PCB production?
Companies can cut costs by improving designs, choosing the right materials, and making more items to save money.
See Also
A Comprehensive Guide to PCBA Manufacturing and Assembly
Key Distinctions Between PCB and PCBA in Electronics
Unveiling the Subtle Differences Between PCBA and PCB
An Overview of SMT Process in PCBA Assembly
Examining Functional and Structural Variations of PCBA and PCB