Circuit boards are very important for electronic devices. They are the main part of many technologies, like smartphones and machines. When problems happen, they can cause big issues. You might wonder, “what does most damage to circuit board?” Common issues include open circuits, short circuits, or bad soldering that mess up electrical signals. These problems can make your PCB less stable and raise the chance of parts failing. Knowing about these problems helps you keep your devices working well.
Key Takeaways
Taking care of circuit boards helps find problems early. This stops bigger issues later on.
Knowing common solder problems, like solder bridges and not enough solder, can make your devices work better.
Aligning parts correctly during assembly is very important. This helps avoid electrical failures and cuts down extra costs.
Cleaning dust and dirt from circuit boards often can stop overheating and help them work better.
Using good design methods and following industry rules can greatly reduce the chance of short circuits.
Solder Issues
Solder issues are some of the most common problems with PCBs. They can hurt how well your circuit board works. Two main soldering problems are solder bridges and not enough solder. Knowing about these issues can help keep your electronic devices reliable.
Solder Bridges
A solder bridge happens when too much solder connects two or more nearby pads or traces. This can create unwanted electrical connections and cause short circuits. Solder bridging usually occurs during soldering, especially with automated machines.
You can find solder bridges using different methods:
Visual Inspection: Use magnifying tools to see surface problems.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): This method quickly finds solder issues in large production.
Functional Testing: Check how well the circuit board works to find hidden problems.
If you see a solder bridge, you can fix it with these methods:
Using Solder Wick (Desoldering Braid): Heat the soldering iron, place the wick over the bridge, and let the iron melt the solder into the wick.
Using a Solder Sucker (Desoldering Pump): Heat the solder, put the sucker over the melted solder, and activate the suction to remove it.
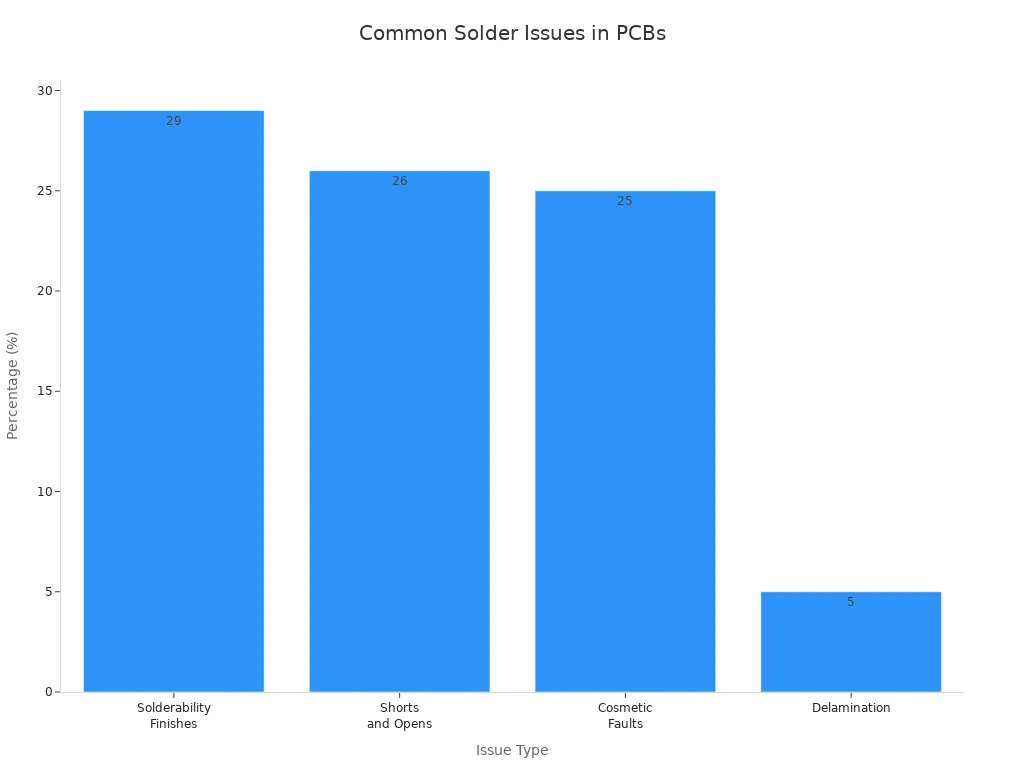
Recent surveys show that solder bridging is a common problem. Here’s a summary of typical solder issues found in printed circuit boards:
Issue Type | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|
Solderability Finishes | |
Shorts and Opens | 26% |
Cosmetic Faults | 25% |
Delamination | 5% |
Insufficient Solder
Insufficient solder happens when there isn’t enough solder to make a strong joint. This can lead to weak joints, which can hurt how well your devices work. Not enough solder can lower reliability and lifespan, possibly causing shorts that can damage the PCB.
Many things can cause insufficient solder:
Cause of Insufficient Solder | Description |
|---|---|
Incorrect stencil design | A bad stencil design can lead to not enough solder paste being applied. |
Low solder paste volume | Not enough solder paste can create weak solder joints. |
Poor wetting | If the solder doesn’t wet the surfaces well, it can lead to not enough solder coverage. |
Heat loss during soldering process | Quick heat loss can stop solder from melting well, causing insufficient solder. |
Component misalignment | Misalignment can create gaps in solder joints, hurting connection quality. |
Inadequate control of soldering process | Not controlling the process well can lead to differences in solder application and quality. |
By fixing these soldering problems, you can improve how your circuit boards work and help them last longer. Regular checks and good soldering methods are key to keeping your PCBs in good shape.
Component Failures
Component failures can really affect how well your circuit board works. Two common problems are cold solder joints and misaligned components. Knowing about these issues helps you keep your PCB reliable.
Cold Solder Joints
Cold solder joints happen when the solder doesn’t melt right during soldering. This creates weak connections that can cause problems. You can find cold solder joints using different methods:
Technique | Description |
|---|---|
Microscopic Examination | Use a low-power loupe or microscope to spot issues like patchy wetting or tiny bubbles. |
Electrical Checking | Use a multimeter to find resistance jumps or signal drop-outs that show incomplete joints. |
Visual Inspection | Look at joint color and shape; check for deformation or light leakage to see bonding quality. |
Testing with a Multimeter | Check continuity or resistance; higher resistance means a cold solder joint needs fixing. |
Cold solder joints can cause big problems in your circuit board. They might make devices malfunction or fail completely. Regular checks and good soldering methods can help stop these issues.
Misaligned Components
Misaligned components can also cause serious problems for your PCB. When components don’t sit right on their pads, they can create various issues:
Impact Type | Description |
|---|---|
Electrical Connection Failures | Misplaced components may not touch solder pads well, causing open circuits or intermittent connections. |
Short Circuits and Overheating | Components too close together can create shorts, leading to overheating and possible PCB failure. |
Signal Integrity Issues | Misplacement can mess up signal integrity, causing delays or jitter in fast circuits. |
Increased Rework Costs and Delays | Fixing misplacements takes time and money, delaying product launches a lot. |
Reduced Product Reliability | Rework can add new defects, lowering overall product reliability and raising field failures. |
To prevent misalignment, make sure to follow proper assembly steps. Regular checks during manufacturing can help catch these problems early.
By fixing cold solder joints and misaligned components, you can greatly improve the reliability and performance of your circuit boards.
Trace Defects
Trace defects can really affect how well your circuit board works. Two common problems are lifted pads and broken traces. Knowing about these issues helps you keep your PCB reliable.
Lifted Pads
Lifted pads happen when the copper pad comes off the PCB surface. This problem can cause bad electrical connections. Several things can cause lifted pads:
Thermal Stress: High heat during assembly can weaken the bond.
Mechanical Stresses: Too much pressure during soldering can lift pads.
Material Quality and Adhesion: Using cheap materials can lead to poor sticking.
Design and Manufacturing Issues: Bad pad design can also cause this issue.
To stop lifted pads, use good materials and follow proper assembly steps. Regular checks can help find these problems early.
Broken Traces
Broken traces are another common PCB problem. They happen when the paths on the circuit board break, stopping the flow of electricity. Fixing broken traces needs careful work. Here are some best tips:
Work Slowly: Rushing can cause mistakes like shorting nearby traces. Take your time.
Use Minimal Solder: Too much solder can create blobs that touch other traces, causing shorts.
Check Trace Ratings: If a trace burned out from high current, use a thicker wire for the jumper to avoid future problems.
Protect the Board: After fixing, put a thin layer of clear nail polish or coating over the area to guard against moisture and rust.
Practice First: If you’re new to soldering, practice on a scrap board before working on your important project.
By fixing lifted pads and broken traces, you can improve the strength and performance of your circuit boards. Regular care and careful assembly will help you avoid these common PCB problems.
Mechanical Damage
Mechanical damage can really hurt how well your circuit board works. Two common problems are cracked PCBs and delamination. Knowing about these issues helps you keep your devices reliable.
Cracked PCBs
Cracked PCBs often happen because of different mechanical stresses. Here are some common reasons:
Thermal Stress: High heat during soldering can cause parts to expand differently. This creates stress in multi-layer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs).
Mechanical Shock and Vibration: If you handle the board wrong, it can cause shocks that crack MLCCs.
Board Flexure: Bending the PCB can put stress on components, especially in larger boards.
Solder Joint Stress: Reflow soldering can push on MLCCs as the solder cools, which might cause cracks.
Cracked PCBs can cause big problems. They may lead to electrical failures, signal issues, and even make devices stop working. You should check your PCBs for cracks often to avoid these problems.
Delamination
Delamination happens when the layers of the PCB come apart. This can be due to bad manufacturing or too much heat. The effects of delamination can be serious. Here’s how it affects your circuit board:
Impact Category | Description |
|---|---|
Electrical Performance Issues | Problems with electrical connections can cause signal issues and more noise. |
Increased Failure Rates | Weaker structure makes PCBs more likely to fail under stress. |
Reduced Reliability and Lifespan | Less reliability can lead to early failures and shorter life for the circuit board. |
Heat Dissipation Problems | Gaps can block heat from escaping, causing thermal stress and failures. |
Difficulties in Repair and Rework | Fixing issues becomes harder because of delamination, making reliable solder joints tough. |
Increased Manufacturing Costs | Higher costs come from fixing or throwing away bad PCBs and warranty claims. |
Impaired Testing and Troubleshooting | Problems with connections make finding faults harder and take more time to test. |
To prevent delamination, use good manufacturing methods and watch the temperature while soldering. By fixing these mechanical damage issues, you can make your circuit boards stronger and better.
Contamination and Corrosion
Contamination and corrosion can hurt how well your circuit board works. Two common causes are dust and debris, along with chemical contamination. Knowing about these issues helps you keep your PCB reliable.
Dust and Debris
Dust buildup can cause big problems for your circuit board. Here are some ways dust and debris can affect performance:
Dust can create layers that block cooling. This can cause overheating.
Dust and dirt can hold moisture, especially in humid places. This moisture can create paths for electricity, causing short circuits.
Dust can block heatsinks, leading to heat buildup and overheating of parts.
In humid conditions, dust can soak up moisture, which may speed up corrosion.
Cleaning your PCB regularly can help stop these problems. Use compressed air or a soft brush to get rid of dust and debris.
Chemical Contamination
Chemical contamination is another big worry for circuit boards. Different sources can bring harmful substances to your PCB:
Ionic contaminants from flux leftovers during assembly can cause corrosion.
Moisture stuck in the layers can create electrical problems.
Etching chemicals are often very conductive and corrosive.
Leftovers from soldering fluxes, like acids and bases, can harm connections.
Residues from cleaning systems can also create issues.
To reduce chemical contamination, use good cleaning methods during assembly. Regular checks can help you find and fix any contamination problems early.
By being careful about dust, debris, and chemical contamination, you can protect your circuit board from defects and make it last longer.
Short Circuits
Short circuits are very common and can seriously damage circuit boards. They happen when unwanted connections form between paths that carry electricity. This can cause too much current to flow, making parts overheat or fail. It can even ruin the whole PCB. Knowing what causes short circuits can help you stop them.
Causes of Short Circuits
Many things can cause short circuits in your circuit board. Here are some main causes:
Solder Bridges: Too much solder can connect pads or traces that shouldn’t touch.
Manufacturing Debris: Leftover materials from making the board can create paths for electricity.
Moisture Ingress: Water can get in through cracks, causing electrical problems.
Conductive Anodic Filament (CAF) Formation: Under certain conditions, CAF can form and cause shorts.
Strain from De-panelization: If stress is too high, it can crack the board and lead to short circuits.
One case showed how dangerous short circuits can be. A public transport communication system failed because of high humidity and voltage. This led to conductive anodic filaments forming, which caused a big problem.
Prevention Techniques
To stop short circuits, you need careful design and assembly. Here are some good techniques you can use:
Design for Manufacturability (DFM): Make sure there is enough space between traces and pads. Keep at least 0.15 mm apart for crowded boards.
Isolation Techniques: Use slots or trenches to keep high-voltage and low-voltage traces apart.
Design Rule Checking (DRC): Use DRC software to check design rules and avoid spacing mistakes.
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Use AOI systems to find soldering problems that might cause short circuits.
Controllable Current Limiting: Add resistors in series with important traces to limit current flow if there’s a fault.
Thermal Overload Protection: Put in thermal protection devices to stop overheating and possible short circuits.
By using these techniques, you can lower the chances of short circuits in your circuit boards. Regular checks and following industry standards will also help keep your PCBs reliable.
In this blog, you learned about common problems in circuit boards. These include solder issues, component failures, trace defects, mechanical damage, contamination, and short circuits. Each problem has specific fixes that can make your PCB more reliable.
To take care of your circuit boards well, keep these important points in mind:
Regular maintenance helps find damage early, stopping bigger problems.
Systematic troubleshooting methods improve how you solve issues quickly.
Use the right tools for accuracy in repairs.
By using these fixes, you can boost the performance of your electronic devices and lower the chance of problems. Remember, being proactive leads to better reliability and longer life for your circuit boards.
FAQ
What is a solder bridge, and how can I fix it?
A solder bridge happens when too much solder connects two pads or traces. You can fix it by using solder wick or a solder sucker to take away the extra solder.
How can I prevent cold solder joints?
To stop cold solder joints, make sure to heat properly while soldering. Use the right amount of solder and check connections closely for quality.
What causes lifted pads on a PCB?
Lifted pads happen because of thermal stress, mechanical pressure, or bad material quality. Use good materials and follow proper assembly steps to avoid this problem.
How do I clean dust and debris from my circuit board?
You can clean dust and debris with compressed air or a soft brush. Cleaning often helps keep performance up and stops overheating.
What should I do if I suspect a short circuit?
If you think there is a short circuit, quickly disconnect the power. Check the board for solder bridges, debris, or moisture. Use a multimeter to look for continuity problems.
See Also
Proven Strategies To Analyze PCBA Failures Effectively
Key Considerations When Selecting Your PCBA Main Board
Understanding PCBA Motherboards: Their Functionality And Importance
Benefits And Challenges Of Flex PCBA In Today’s Electronics
Frequently Utilized PCBA Components And Their Essential Roles