
An electronic board is like the heart of your devices. You use these boards every day. They are in your smartphone, computer, and smart watch. Almost all modern electronics need electronic boards. Printed circuit boards are the backbone for about 70% of devices. This is true for consumer, computer, and telecommunications products. The job of pcbs is more than just connecting parts. They help electronics get smaller and work better. Better designs and new materials help electronic boards do more. They let more features fit into tiny spaces. This makes gadgets stronger and more useful than before.
Key Takeaways
Electronic boards link and keep parts together in devices. They help make gadgets smaller and smarter. Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the most used type. They help devices work well and last a long time. Different boards have different jobs. Breadboards are for testing ideas. PCBs are for strong and lasting products. Specialized boards are for custom projects. Quality control and good design keep electronic boards safe. This is important for everyday and medical devices. New materials and designs help future boards get smaller and bend. They also make boards stronger for smart technology.
Electronic Board Basics
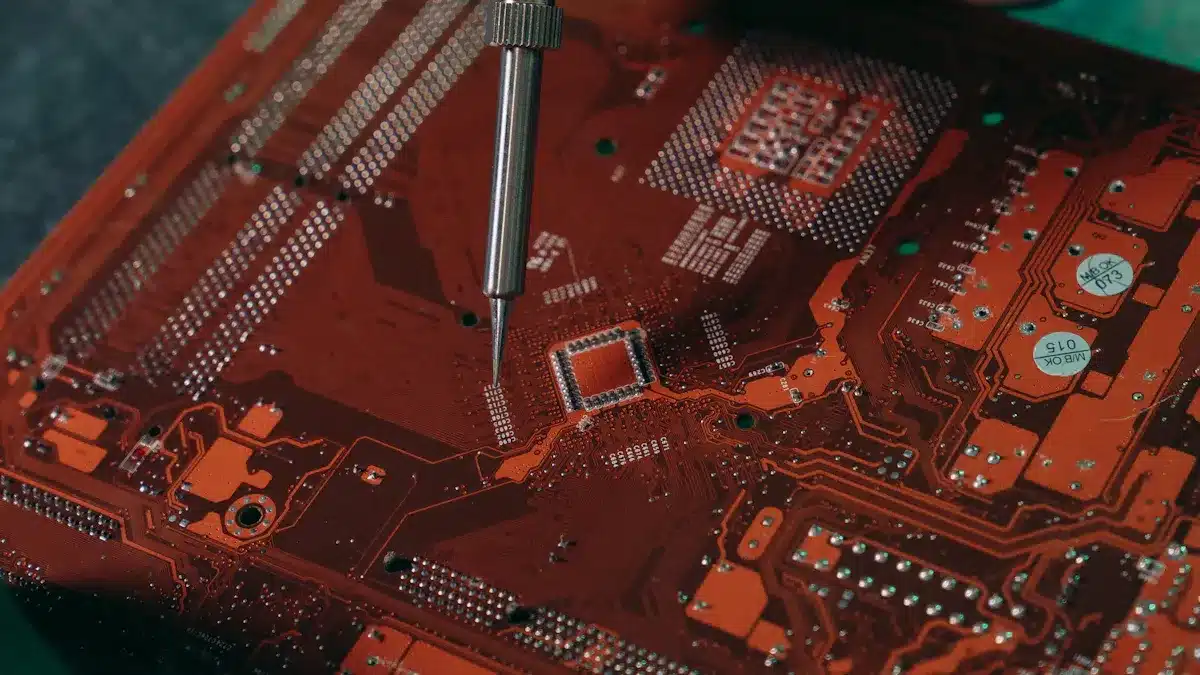
What Is an Electronic Board
An electronic board is where all the parts of a device come together. It holds and connects the pieces so they can work as one. If you open up most electronics, you will see these boards inside.
An electronic board is a place to put and link electronic parts.
The board has a base, usually made from plastic or fiberglass, to hold everything.
You will see resistors, capacitors, transistors, diodes, and microprocessors on the board.
Copper lines run across the board and let electricity move between the parts.
The main job of an electronic board is to link all the parts and let signals pass between them. This setup lets complex circuits fit into small places. Without electronic circuit boards, your devices would not be as small or work as well.
Note: The motherboard in your computer is an electronic board. It links the CPU, memory, storage, and other parts so they can talk and share power.
Structure and Components
Electronic circuit boards have layers. Each layer does something special. The bottom layer, called the substrate, makes the board strong and keeps it from carrying electricity. Most boards use fiberglass with epoxy resin, called FR-4, because it is tough and can handle heat. Some boards use bendy plastic or metal for special jobs.
Material Category | Examples/Types | Why Use It? |
|---|---|---|
Substrate Materials | Insulation, strength, heat control, chemical resistance, cost, and use in high-temp devices | |
Conductive Material | Copper foil | Great for carrying electricity and heat |
Surface Finishes | ENIG, HASL, OSP, Immersion Silver | Protects copper from rust and helps with soldering |
Solder Mask | Epoxy resin-based inks | Shields copper traces and helps with soldering |
Silkscreen | Non-conductive epoxy ink | Labels parts and gives information |
The most important part of electronic circuit boards is the copper traces. These thin lines are like roads for electricity. How wide and close they are, and how they are placed, changes how much current they can carry and how well the board works. Pads are flat spots where you can solder parts. Vias are tiny holes that let signals go from one layer to another, so you can make more complex circuits in a small space.
Most boards have a solder mask. This green (or sometimes other color) layer covers the copper lines and keeps them safe. The silkscreen layer adds labels so you know where parts go and what they do.
Electronic circuit boards use copper because it is good at carrying electricity and heat. Good trace design stops problems like getting too hot, losing signals, or having interference. Using new materials or special designs lets you make boards that are smaller and work better. This is why today’s electronics can have so many features in such small devices.
Types of Electronic Circuit Boards
When you look at electronic circuit boards, you find a few main types. Each type is built in its own way and has a special job. People use these boards in many things, from easy projects to high-tech devices.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
A printed circuit board is the type you see most often. PCBs have layers of copper lines that link parts together. You can find them in phones, computers, and medical tools. PCBs come as single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer boards. These boards work for both simple and hard circuits. They give strong, lasting links and help devices stay small and work well.
PCBs are needed for things that must be tough and small. You find them in factory machines, planes, and security tools.
Structural Features | Application Highlights | |
|---|---|---|
PCB | Custom-made, copper layers, solder mask, silkscreen; handles hard and fast circuits; strong soldered links. | Good for finished products, tricky test models, and making lots of items; gives trust, strength, and small size. |
Breadboards and Prototyping Boards
Breadboards let you build and try out circuits fast. You do not need to solder, so you can change your setup easily. Breadboards have metal clips under holes to join parts. These boards are best for low-power and slow circuits. People use them in schools or when trying new ideas.
You can use them again for other projects.
They are not good for finished products or strong circuits.
Board Type | Structure Description | Application and Usage |
|---|---|---|
Breadboard | No solder, holes with metal clips, easy inside links; for through-hole parts. | Great for quick tests, learning, and trying ideas; not for strong or fast circuits. |
Specialized Boards
Specialized boards are between breadboards and PCBs. These include perfboards, stripboards, and wire-wrap boards. You use them when you want a circuit that lasts longer than a breadboard but is not as fixed as a pcb. Some pcbs, like bendy or metal-core boards, are used in cars, hospitals, or planes.
Board Type | Structure Description | Application and Usage |
|---|---|---|
Specialized Boards | Needs solder or wire wrap; stronger than breadboards but not as strong as PCBs. | Used for test models that last longer or special jobs; mix tricky work and easy changes. |
You see electronic circuit boards in many fields. The chart below shows where PCBs are used most:
You pick different boards for different needs. Breadboards help you learn and test ideas. PCBs make devices strong and small. Specialized boards let you make custom projects. Picking the right board helps your electronics work better and last longer.
Electronic Circuit Board in Practice
Everyday Devices
You use electronic circuit boards all the time, even if you do not see them. These boards are inside your phone, tablet, and computer. They are also in cameras, microphones, and LED lights. The electronic circuit board links all the parts inside these devices. This lets the parts share information and work together. Because of this, your gadgets can be smaller and lighter. They can also do more things at once.
Here is a table that shows how electronic circuit boards help different devices:
Device Category | Examples of Devices | Role of PCBs in Device Functionality |
|---|---|---|
Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, tablets, computers, cameras, microphones | PCBs connect parts, control power, and let devices be small and do many things. |
Automotive Electronics | Navigation systems, media equipment, control systems | PCBs handle signals for navigation, music, and controls, making cars safer and better to drive. |
LED Lighting | Home lighting, storefront displays, car lights, computer screens | PCBs help move heat away and control power, so LEDs last longer and work well. |
Security Systems | Electronic locks, security cameras, smoke detectors | PCBs help security devices work well, even in hard places. |
PCBs are the main support for consumer electronics. They make sure every part works right.
Industrial and Medical Uses
You can find electronic circuit boards in many factory machines and medical tools. In factories, these boards control robots, sensors, and safety systems. They help machines work safely and without problems. In hospitals, electronic circuit boards are in pacemakers, blood pressure monitors, and MRI scanners. These boards must be small, strong, and very dependable. Surface Mount Technology lets more parts fit on a board. This makes medical devices lighter and safer. Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs can bend or fit into tiny spaces. This is important for health monitors you wear or for implants.
Medical equipment needs electronic circuit boards for correct readings and to keep patients safe. The boards help with wireless checks and quick data sharing. This helps doctors make good choices. Careful design and testing make sure these boards follow strict safety rules.
Communication and Automotive
Modern cars and communication systems need electronic circuit boards to work. In cars, these boards link sensors, control units, and safety systems. They help control the engine, brakes, and even music or video. Good PCB design keeps your car safe and working well, even with heat or shaking.
Communication networks in cars use electronic circuit boards to send data fast between parts. This lets your car have GPS, smart driving, and updates in real time. In electronics, these boards also power routers, cell towers, and other things that keep you connected.
The electronic circuit board in practice is in almost every part of your life. It helps electronics be smarter, safer, and more dependable.
PCB Manufacturing

Design Process
When you design a pcb, you follow clear steps. First, you figure out what your circuit needs. You look at things like voltage and current. Then, you make a schematic to show how parts connect. You use special software, such as Altium Designer or KiCad EDA. These programs help you draw and place each part. They also check for mistakes and show 3D views. The software has many parts in its library. After you finish, you add labels and check the rules. You make files called Gerbers for the manufacturer.
Tip: Design software with built-in checks helps you find mistakes early. This makes your pcb work better.
Production Steps
After you finish the design, the pcb goes to production. First, machines cut copper, resin, and glass to the right size. Holes are drilled for parts and connections. Copper layers are added to make the circuit paths. A solder mask covers the copper to keep it safe. Labels are printed on the board for easy assembly. Machines put parts on the board, and soldering holds them in place. The board goes through lamination, etching, and plating. These steps make strong and correct connections. At the end, the board is shaped, cleaned, and made ready for testing.
Quality Control
You want your pcb to work every time you use it. Quality control checks each step in the process. AOI uses cameras to find problems on the surface. X-ray inspection looks inside the board for hidden issues. ICT checks if each part works and connects right. Environmental tests put the pcb in heat, cold, and shaking. This makes sure it will last. Workers also look for small flaws by eye. Manufacturers follow rules like IPC-A-600 and ISO 9001. These steps help you get safe and strong printed circuit boards.
Quality Control Method | Purpose and Description |
|---|---|
AOI | Uses cameras to find surface problems and missing parts |
X-ray Inspection | Looks inside the board for hidden issues |
Checks if each part and circuit works right | |
Environmental Stress Testing | Tests if the pcb can handle tough places |
Workers look for scratches, cracks, or parts that do not line up | |
Standards Compliance | Follows rules like IPC-A-600 and ISO 9001 for safety and quality |
Remember: Careful testing and following rules help your pcb work well in any device.
Importance and Trends
Benefits in Modern Electronics
You see electronic boards in almost every device today. These boards help make gadgets smaller and lighter. PCBs are strong and can handle heat and shaking. This means your devices last longer and work well. It is easy to fix things because the layout is simple. You can find and change parts quickly. PCBs help stop signal loss and noise, so devices work better. Companies save money by making many boards at once.
Small and light gadgets
Strong and last a long time
Easy to fix and keep working
Work better and use less power
Cheaper to make
PCBs help engineers build new technology. You get faster phones, smart cars, and safe medical tools. Many people get jobs in this industry, like engineers and factory workers.
Innovation and Miniaturization
Your devices keep getting smaller and smarter each year. This is because of new ideas in board design. PCBs now fit more circuits in less space. Some boards can bend or fold, so devices can too. Engineers can put parts inside the board to save space and make things work better.
Miniaturization lets you wear smartwatches and use wireless earbuds. You can even have foldable phones. These changes help make better boards for the future.
New memory chips store data faster and safer. Boards like Bullseye Evaluation Board help connect your home to the Internet of Things. These new things make your electronics stronger and more useful.
Future Developments
You will see even more changes in electronic boards soon. Companies use new materials like ceramics and Teflon. These help boards handle heat and keep signals strong. Flexible and 3D-printed boards will let you use electronics in new ways. You might see them in smart clothes or medical patches.
Parts inside boards will save space and make things faster.
Green ways to make boards will help the planet.
Artificial intelligence will help design better boards.
You will see these trends in electric cars, 5G, and medical tools. The future will bring smarter, safer, and more connected devices to your life.
You use technology that you cannot see every day. Electronic boards help your devices work well and last longer. They do this by using strong designs and careful tests. These boards also help make gadgets smaller and lighter. They let your devices do more things. When you learn about electronics, you get better at solving problems. You also become more creative. Try easy projects and learn how to use new tools. Always stay curious about what will come next. 🚀
FAQ
What is the main job of a printed circuit board (PCB)?
A PCB connects and supports electronic parts. You use it to let electricity flow between components. This helps your device work as one system.
Can you reuse a breadboard for different projects?
Yes, you can reuse a breadboard many times. You do not need to solder parts. You just plug in and remove components as you test new ideas.
Why do most PCBs look green?
Most PCBs look green because of the solder mask. This layer protects copper traces. Manufacturers use green because it is easy to see and inspect.
How do you know if a PCB is high quality?
You check for smooth edges, clear labels, and no missing parts. High-quality PCBs pass tests like AOI and ICT. They also follow safety standards.
See Also
Exploring The Meaning And Importance Of PCBA In Electronics
What PCBA Means And Its Function In Electronic Devices
A Clear Guide To PCBA Definition And Its Electronics Uses
An Overview Of EMS And PCBA Solutions For Modern Electronics