IIoT Hardware Manufacturing involves creating physical tools and sensors that connect machines, systems, and processes within factories. These devices play a crucial role in collecting, analyzing, and sharing data rapidly during production. By leveraging IIoT hardware, manufacturers can enhance efficiency and drive innovation. For instance, predictive maintenance enabled by IIoT hardware can prevent 70% of equipment failures while reducing maintenance costs by 25%. Additionally, companies utilizing data-as-a-service (DaaS) experience revenue growth 2.8 times faster and achieve 3.1 times higher profits. With the global IIoT market projected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2028, IIoT Hardware Manufacturing is revolutionizing the way factories operate.
Key Takeaways
IIoT devices help factories work better by gathering live data. This data checks machines and stops expensive breakdowns.
Predictive maintenance using IIoT lowers repair costs by 30%. It also cuts downtime by up to 30%, making machines work better with fewer mistakes.
Smart tools like sensors and RFID tags improve stock tracking. They also save energy, making factories cheaper to run and eco-friendly.
Factories using IIoT can quickly meet customer needs for custom items. They can make unique products fast without slowing down.
To use IIoT well, factories should start small. They need to train workers and protect important data with strong cybersecurity.
Transformative Impact of IIoT Hardware in Manufacturing

Real-time Data Collection and Monitoring
IIoT hardware helps gather and study live data from factory systems. This changes how factories check machines and production performance. Smart sensors inside machines watch things like heat, shaking, and pressure. These sensors keep machines running well and spot problems early.
For example, Caterpillar uses IIoT to check its machines from far away. This helps fix issues quickly, cutting downtime and making customers happy. GE’s Predix platform uses IIoT sensors in wind turbines to make more power. It also lowers repair costs and boosts energy production.
Real-time data sharing does more than just monitoring. A Deloitte study says unplanned downtime costs factories $50 billion yearly. Using IIoT can stop 75% of quality problems with live monitoring and data analysis. This helps factories work better and avoid interruptions.
Statistic | Source | Year |
|---|---|---|
Unplanned downtime costs factories $50 billion yearly | Deloitte | 2021 |
75% of quality issues can be stopped with live monitoring | Quality Magazine Industry Survey | 2022 |
Predictive Maintenance and Downtime Reduction
Predictive maintenance is a big benefit of IIoT hardware. It uses sensor data to predict when machines might break. Repairs can then be planned during quiet times. This saves time, cuts repair costs, and makes machines last longer.
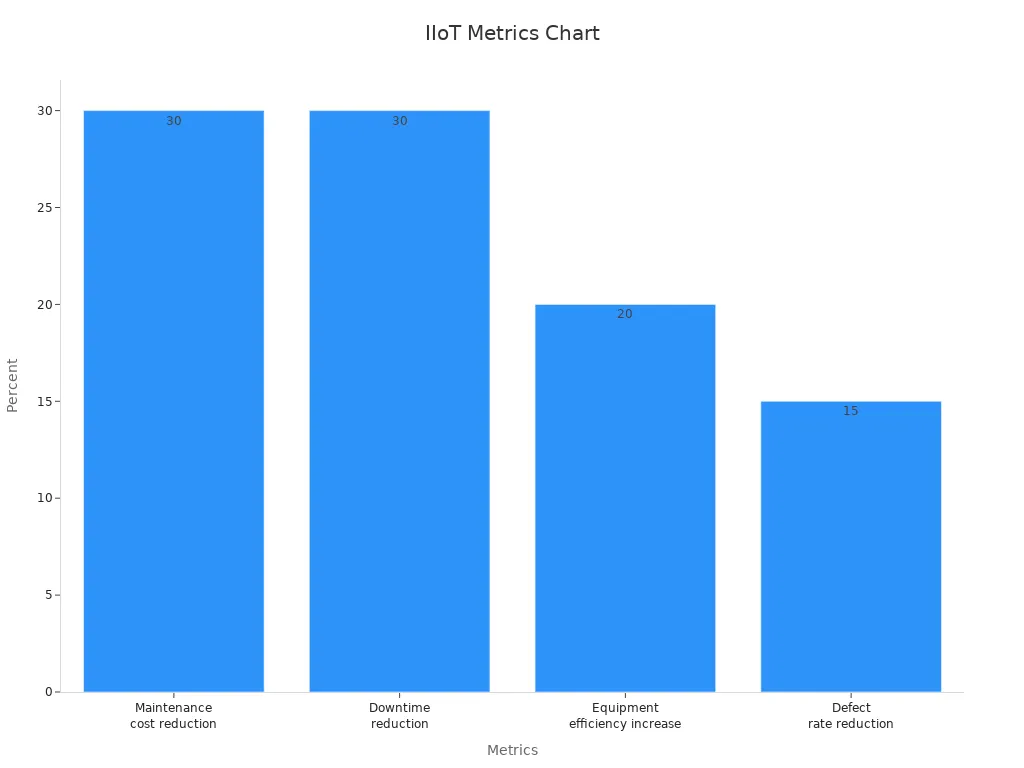
Factories using predictive maintenance save about 30% on repairs yearly. They also cut downtime by up to 30%. Machine efficiency improves by 20%, and defects drop by 15%. These numbers show how IIoT improves factory performance.
Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Maintenance cost savings | About 30% yearly |
Downtime reduction | Up to 30% |
Machine efficiency boost | 20% |
Defect rate drop | 15% |
Downtime hours saved yearly | 100 hours |
Predictive maintenance also tracks equipment in real time. Repairs during quiet times keep work flowing smoothly. This automation makes factories more productive and reliable.
Enhancing Operational Efficiency
IIoT hardware helps factories work better in many ways. Smart sensors, RFID tags, and smart meters improve production, inventory, and energy use.
For example, RFID tags follow materials during production. This stops overstocking and keeps inventory just right. Smart meters check energy use, finding waste and saving power. These tools make factories greener and save money.
Improvement Area | IIoT Implementation Description |
|---|---|
Real-time Monitoring | Sensors check heat and vibration to spot problems early. |
Predictive Maintenance | Sensors predict breakdowns, allowing timely repairs and less downtime. |
Inventory Management | RFID tags track materials, avoiding too much stock and keeping inventory balanced. |
Energy Management | Smart meters find energy waste and help save power. |
Digital ANDON systems show how IIoT improves factory efficiency. Replacing old ANDON boards with digital ones boosts production and speeds up problem-solving.
Metric | Before Digital ANDON | After Digital ANDON |
|---|---|---|
Machine Downtime | 15% | 5% |
Production Output | 250 units/hour | 320 units/hour |
Response Time to Issues | 30 min | 5 min |
Using IIoT hardware can turn factories into smart workplaces. This change makes factories more efficient and ready for future challenges.
IIoT Hardware and Mass Customization
Meeting Consumer Demands with Customization
IIoT hardware is changing how factories make personalized products. Over half of customers now want items made just for them. This makes customization important for growing businesses. Using IIoT, factories can adjust systems to handle custom orders easily. They can make different products at the same time without stopping production. This saves money and makes work more flexible.
Adidas uses IIoT in its Speed Factory to make custom shoes. These shoes match what each customer wants. The factory combines fast production with careful personalization. IIoT helps factories like this make unique products while staying efficient.
Flexible Manufacturing Processes
IIoT hardware helps factories quickly adapt to new customer needs. Businesses using IIoT can make custom goods without losing speed or quality. For example, Siemens’ Smart Factory uses IIoT to create special medical devices. This lets factories meet many customer demands and stay competitive.
Mass customization mixes fast production with personalized products. IIoT hardware connects machines and systems to make this possible. Smart sensors and live monitoring tools help switch between product types smoothly. This reduces downtime and increases production.
Examples of Successful IIoT Applications
Real-world examples show how IIoT improves manufacturing. Companies using IIoT report better efficiency and greener practices. For example:
Application Area | Benefits |
|---|---|
Machine Monitoring | Better equipment performance and smoother processes. |
Quality Assurance | Sensors find defects early. |
Predictive Maintenance | Less downtime and lower repair costs. |
Overall Performance | 20% lower costs and 30% fewer emissions. |
Factories using IIoT gain two extra weeks of production each year. These tools make manufacturing smarter and help businesses stay ahead.
Overcoming Challenges in IIoT Hardware Adoption
Addressing Security and Privacy Concerns
Using IIoT hardware can bring security and privacy problems. Factories must keep sensitive data safe from cyberattacks. Connected IIoT systems are at higher risk of hacking. Strong security measures are needed to protect real-time monitoring tools.
The Mean Time to Detection (MTTD) shows how fast issues are found. Quick detection helps stop data loss or damage. The Mean Time to Response (MTTR) measures how fast problems are fixed. Companies focusing on these metrics face fewer breaches and losses.
Metric | What It Measures |
|---|---|
Mean Time to Detection (MTTD) | Time taken to find a security problem. |
Mean Time to Response (MTTR) | Time taken to fix a detected security issue. |
Number of Incidents | Total security problems over a set time. |
Successful Breaches | Security problems that led to data being stolen or damaged. |
Closed Incidents | Security problems that were solved. |
Loss or Damage | Amount of harm caused by security problems. |
Thwarted Attempts | Number of hacking attempts stopped before causing harm. |
To stay safe, factories should use encryption, multi-factor logins, and regular security checks. Training workers on cybersecurity also reduces risks. These steps help protect IIoT systems and build trust in factory operations.
Integrating IIoT with Legacy Systems
Adding IIoT hardware to old factory systems can be hard. Older systems often don’t work well with modern tools. This causes problems with sharing data and connecting devices.
Only 30% of factories fully use IIoT, while 67% struggle with integration. Also, 63% of companies can’t expand IIoT projects beyond testing. These numbers show why careful planning is important.
Scalability Problems: IIoT tools may not grow with business needs.
Compatibility Issues: Old systems may not connect with new IIoT tools.
Skill Gaps: Workers may lack the knowledge to use IIoT properly.
Factories should start small by using IIoT in key areas like predictive maintenance. Slowly add IIoT to other parts of production. This step-by-step plan helps fix compatibility problems and avoids major disruptions.
Managing Risks While Innovating
Making new IIoT hardware comes with challenges. High costs, strict rules, and complex systems can make it hard to succeed. Factories must balance innovation with possible risks.
For example, privacy rules require factories to protect data. Breaking these rules can lead to fines and hurt reputations. Keeping IIoT hardware running smoothly also needs clear plans. Without good planning, systems can become too hard to manage.
To handle risks, factories should train workers to use IIoT tools. Training programs can teach employees to study data and use new technology. Working with tech providers ensures systems stay updated and follow rules. These steps help factories innovate while avoiding big problems.
Human Oversight in IIoT Systems
Balancing Automation with Human Expertise
Automation has changed how factories work today. But, using only automation without human checks can cause mistakes. People are important to make sure IIoT systems work well and responsibly. For example, IIoT systems are great at studying live data. However, they might not understand unusual situations. Human knowledge helps check these results and ensures decisions are fair and correct.
A Takepoint Research study shows 80% of cybersecurity experts see AI benefits but also risks. Factories with human checks (56%) do better than those without (44%). They are more accurate and less biased. By mixing automation with human skills, factories can work better and avoid problems.
Decision-making in Data-driven Manufacturing
Making decisions using data is key in modern factories. IIoT hardware gives useful information by watching machines, predicting issues, and improving production. This saves money and boosts efficiency.
Here are some improvements from data-driven manufacturing:
Benefit | Improvement Metrics |
|---|---|
Increased Efficiency | |
12% better labor productivity | |
25% fewer unplanned machine stops | |
Cost Savings | 14-23% lower maintenance costs |
18% less energy used | |
12% less raw material wasted | |
Enhanced Safety | 27% fewer workplace accidents |
32% drop in near-miss incidents | |
41% better hazard spotting | |
Improved Quality | 32% fewer defects |
47% fewer customer complaints about quality | |
29% fewer warranty claims |
These numbers show how IIoT hardware helps factories make smart choices. It improves safety and productivity.
Workforce Training and Upskilling
As IIoT systems grow smarter, learning new skills is vital. Training on IIoT tools helps workers check machines, study data, and fix problems. Learning new skills keeps workers valuable even as automation grows.
For example, knowing how to read live data from IIoT sensors can help spot machine problems early. Learning predictive maintenance tools can make machines last longer and reduce downtime. By improving skills, workers can stay ahead in the changing factory world.
Future of IIoT Hardware in Manufacturing
Fully Connected Smart Factories
Smart factories are the future of manufacturing. Here, machines and systems work together smoothly. Using technologies like IoT, AI, and robotics improves production and saves time. Industries like cars and planes are leading this change. They need faster production and better supply tracking. Governments in advanced countries are also supporting smart factories. This helps increase productivity and use less energy.
A study by Hu et al. (2024) showed smart factories cut pollution. They used advanced tools to prove these factories help the environment.
Adding IIoT hardware to smart factories allows live monitoring and better maintenance. It also makes creating custom products easier. These changes improve production and help make factories greener and more flexible.
Impact on Supply Chains and Global Trade
IIoT is changing how supply chains work. It connects everything from raw materials to finished products. Smart sensors check machines to avoid delays and keep things running. Live data helps track items, manage stock, and deliver on time. This makes decisions easier and improves teamwork in the supply chain.
Full tracking ensures rules are followed and products are better.
Data analysis predicts demand, making customers happier.
Safe data sharing builds partnerships and new business ideas.
Using IIoT hardware makes supply chains faster and more flexible. These tools simplify work and open doors for new ideas and growth.
Emerging IIoT Trends and Technologies
The future of IIoT depends on new ideas. Trends like smarter maintenance, AI tools, and energy-saving systems are changing factories. For example, predictive maintenance stops 70% of breakdowns and cuts repair costs by 25%. Automation has also reduced errors by 65%, improving quality.
Benefit Type | Documented Outcome |
|---|---|
Quality Improvement | 65% fewer errors thanks to automation and digitization |
Predictive Maintenance | 70% fewer breakdowns and 25% lower repair costs |
Energy Cost Reduction | 40% less energy used with live IoT monitoring |
These changes show how powerful IIoT hardware can be. By following these trends, factories can stay competitive and succeed in the future.
IIoT hardware is changing how factories make and use machines. Smart tools help factories work faster, meet customer needs, and create new ideas. Today, 95% of factories use smart tools, but only 44% use the data well. The IIoT market could grow to $1.51 trillion by 2030, showing its importance. To stay ahead, factories must solve problems like security and old system updates. Using IIoT makes machines smarter, production easier, and factories ready for the future.
Statistic/Insight | Value/Projection |
|---|---|
Factories using smart tools | 95% |
Factories using data well | 44% |
IIoT market size by 2030 | $1.51 trillion |
Market growth from 2023 to 2028 | $147.2 billion to $391.8 billion |
Yearly growth rate (CAGR) | 21.6% |
FAQ
What is IIoT hardware, and why does it matter in factories?
IIoT hardware includes sensors and devices that link machines together. It collects live data, boosts efficiency, and cuts downtime. This technology turns factories into smarter and more productive places.
How does IIoT hardware make factories work better?
IIoT hardware watches machines, tracks energy use, and manages supplies. These tools cut waste, improve production, and save money. They make factory operations quicker and more dependable.
Can IIoT hardware work with older factory equipment?
Yes, but it can be tricky to connect them. Start small by using IIoT for tasks like predicting repairs. Slowly add more tools to avoid problems and ensure they work well together.
What are the dangers of using IIoT hardware?
IIoT systems can face hacking and data theft risks. Protect your factory by using strong passwords, encryption, and regular security checks. Teaching workers about cybersecurity also helps keep systems safe.
How does IIoT hardware help with custom products?
IIoT hardware allows factories to make personalized items easily. It lets you create custom goods without slowing down production. This helps meet customer needs while staying efficient and high-quality.
See Also
The Importance of Custom PCBA in Today’s Electronics Industry
PCBA’s Role in Elevating Today’s Electronics Innovations
The Pros and Cons of Flex PCBA in Electronics
Exploring Android PCBA’s Impact on Current Technology Trends
Essential Strategies for Overcoming PCBA Manufacturing Obstacles