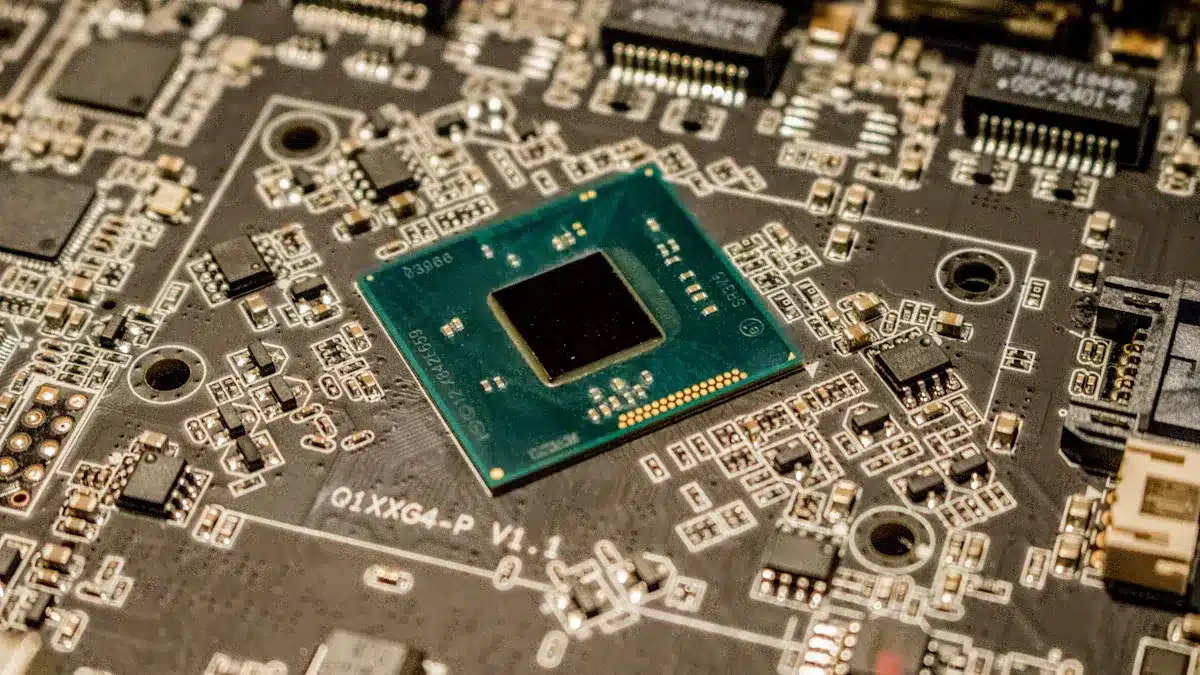
PCB means Printed Circuit Board in electronics. If you’re wondering what is PCB stand for, it refers to the essential board that connects electronic components. You find PCB technology in almost every device. These boards let many parts fit into small spaces, helping devices get smaller and stronger. If you want to know how your phone or computer works, you should learn about PCB design. Medical equipment also uses PCB construction. Making electronics smaller and more reliable needs new ideas. Surface mount technology and flexible PCB structures help with this.
Knowing what PCB stands for gives you a good start in electronics. You will see how PCB features help devices work better and last longer.
Key Takeaways
PCB means Printed Circuit Board. It is the base that holds and connects electronic parts in devices. PCBs use copper traces to move electricity. They keep parts neat and avoid messy wires. There are different PCB types. These include single-sided, double-sided, multilayer, flexible, and rigid. Each type fits different needs and device sizes. Materials like FR-4, polyimide, and ceramic make PCBs strong. These materials help PCBs resist heat and work in many ways. PCBs are important in electronics we use every day. They are also in cars, factories, and medical devices. PCBs help gadgets become smaller, faster, and more reliable.
What Is PCB Stand For
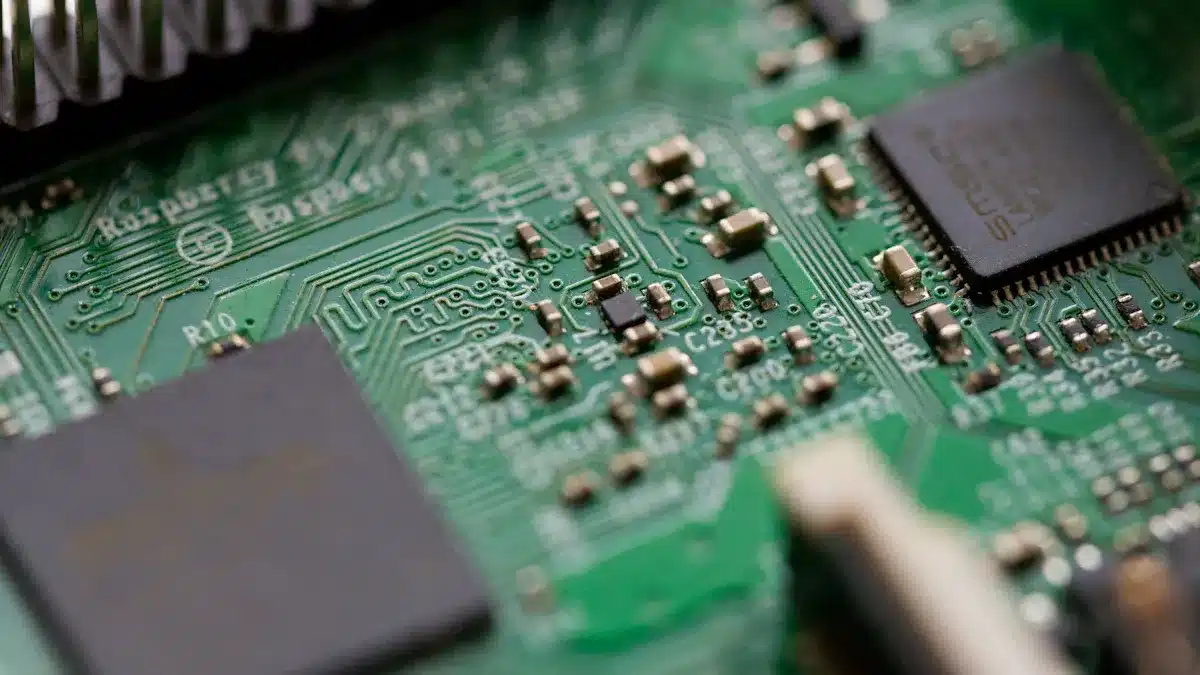
PCB Meaning
When you ask what is pcb stand for, you discover that it means printed circuit board. You see this term everywhere in electronics. A pcb is a flat board that holds and connects electronic parts. You use a pcb to make sure each part works together in a device. The board uses copper lines to link components like resistors, capacitors, and chips. These copper paths let electricity flow between parts. You find a pcb inside your phone, computer, and even your TV remote.
A pcb gives mechanical support to all the parts. You do not need messy wires because the copper traces do the job. You can think of a pcb as the backbone of any electronic device. When you look inside a gadget, you see a green or blue pc board with tiny lines and dots. These lines are copper traces, and the dots are pads for soldering parts. You use a pcb to keep everything organized and working smoothly.
Tip: If you want to build your own electronic project, you start with a pcb. It helps you connect parts safely and neatly.
Printed Circuit Board Definition
You may wonder what is pcb stand for when you see a pc board in a device. The printed circuit board is a special board made from layers of insulating material and copper. The copper forms the pathways for electricity. The insulating layers keep the electricity from going where it should not. You use a printed circuit board to mount and connect all the parts needed for a circuit.
Here is a simple table to show what makes up a pcb:
Layer | Purpose |
|---|---|
Insulating Substrate | Holds everything together |
Copper Traces | Carry electrical signals |
Solder Pads | Attach components |
A printed circuit board does not have any parts on it at first. You add the parts later to make a working device. You use a pcb to make sure each part gets power and signals. The pc board is different from other carriers because it is just the base. When you add parts, it becomes a complete assembly.
You see that what is pcb stand for is more than just a name. It is the foundation of modern electronics. You rely on pc boards to make devices smaller, faster, and more reliable. Every time you use a gadget, you depend on the pcb inside to keep things running.
A pcb acts as a platform for mounting parts.
It provides copper traces for electrical connections.
You use a pc board to organize and support components.
The printed circuit board makes mass production possible.
When you learn what is pcb stand for, you understand how electronic devices work. You see why the pcb is so important in technology today.
Circuit Board Structure
PCB Materials
When you see a circuit board, it is not just green. The materials inside a pcb make it strong and safe. Most circuit boards use FR-4 as the main layer. FR-4 is fiberglass mixed with epoxy resin. This makes the pcb strong and stops it from burning. About 70% of circuit boards use FR-4. It is cheap and works for many things. FR-4 can handle heat, water, and chemicals. This helps your devices last longer.
Some pcb designs need other materials. Flexible circuit boards use polyimide or PTFE. Polyimide bends and does not break. It can take high heat. PTFE, or Teflon, is good for high-frequency circuits. High-power or LED boards use ceramic like aluminum oxide. Each material helps the pcb do its job. You find them in toys and medical devices.
Here is a table to compare common pcb materials:
Material | Key Features |
|---|---|
FR-4 | Strong, fire-resistant, cost-effective |
Polyimide | Flexible, heat and chemical resistant |
PTFE | High-frequency, temperature stable |
Aluminum Oxide | High thermal conductivity, used in LED boards |
Tip: When you start pcb design, pick the right material. This helps your circuit board work for your project.
Layers and Conductive Paths
A pcb is not just a flat board. It has layers that help your ideas work. The middle of every circuit board is a non-conductive base, usually FR-4. Thin copper layers go on top of this base. These copper layers let electricity move. A single-sided pcb has copper on one side. Double-sided and multilayer boards have copper on both sides or inside.
Manufacturers press these layers together with heat. This makes the board strong and steady. The copper layers act like roads for electricity. These roads, called traces, link parts like resistors and chips. Vias are tiny holes filled with copper. They let signals move between layers in a multilayer pcb.
A solder mask covers the copper to stop short circuits. It also protects the traces. The white marks on a circuit board are the silkscreen. This helps you put and find parts during pcb design.
Copper traces move signals and power between parts.
The layers keep the circuit board strong and neat.
Vias link layers, so complex circuits can work.
You need good design for these layers and paths. This keeps your devices safe and working well. Good pcb design uses these features to stop mistakes and keep signals clear.
Types of Printed Circuit Board
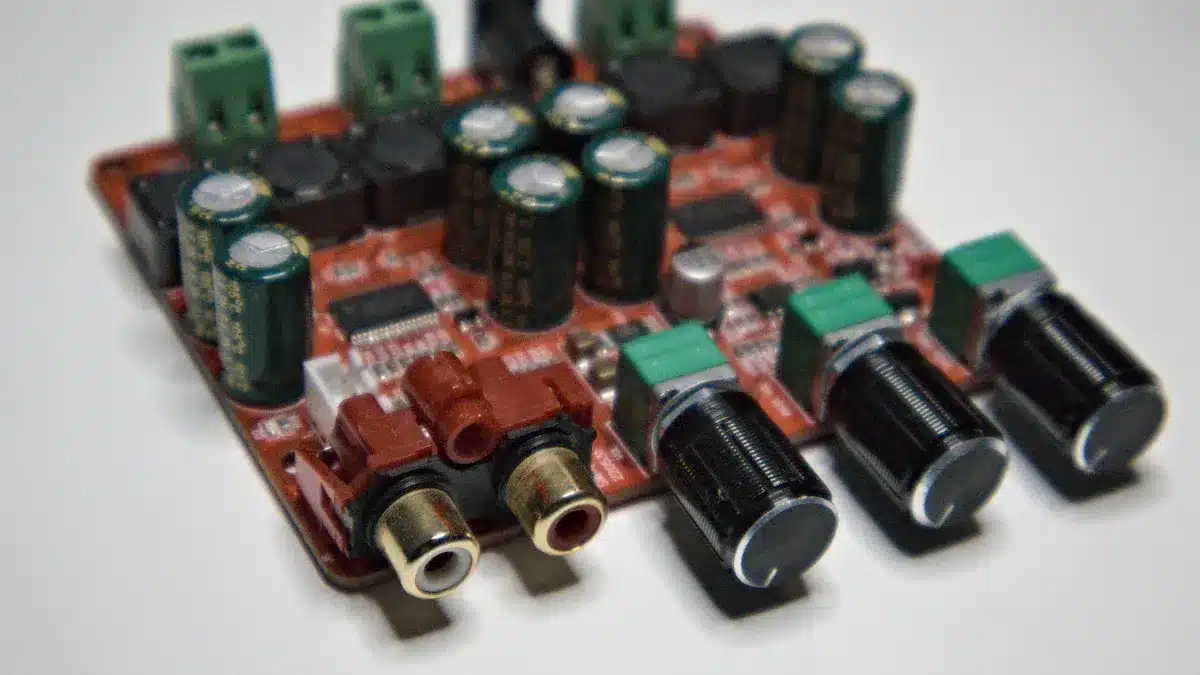
Single-Sided and Double-Sided
Single-sided and double-sided pcbs are very common. A single-sided pcb has copper and parts on one side only. This makes it simple and cheap to make. You see single-sided pcbs in things like calculators and remotes. They are good for basic and low-cost devices.
Double-sided pcbs have copper on both sides of the board. Vias connect the two sides together. This lets you add more parts and traces. Double-sided pcbs help you build more complex circuits. You find them in car dashboards and vending machines. These boards give better signals and handle heat better.
Here is a table to compare them:
Aspect | Single-Sided PCB | Double-Sided PCB |
|---|---|---|
Structure | Copper on one side | Copper on both sides, connected by vias |
Cost | Lower | Higher |
Complexity | Simple | More complex |
Application | Calculators, LED panels | Car dashboards, industrial controls |
Tip: Use single-sided for easy projects. Pick double-sided for more features.
Multilayer PCB
If you need to fit many parts in a small space, use a multilayer pcb. This type has many layers of copper and insulation stacked together. Some multilayer pcbs have 4, 6, or even 12 layers. Each layer helps you add more signals and power lines. Multilayer pcbs are used in smartphones and computers.
Multilayer pcbs give better signal quality and less noise. The extra layers help with heat and power. You can make fast and powerful circuits with them. Single- or double-sided boards cannot do this. Multilayer pcbs are important for small and strong electronics.
Multilayer pcbs fit more parts in less space.
They give better control of power and signals.
These pcbs are strong and work well in advanced devices.
Flexible and Rigid PCB
You can pick flexible or rigid pcbs for your project. A flexible pcb can bend and twist to fit small spaces. You see flexible pcbs in wearables, medical tools, and cameras. They save space and are light, but cost more and hold fewer parts.
A rigid pcb stays flat and does not bend. Most electronics and machines use rigid pcbs. They can hold more parts and are easy to fix. Rigid pcbs are cheaper for big orders but cannot bend.
Type | Advantages | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
Flexible PCB | Bends, saves space, light weight | Wearables, medical, cars |
Rigid PCB | Strong, supports more parts | Phones, computers, tools |
Note: Flexible pcbs are good for small, moving gadgets. Rigid pcbs are best for strong and steady products.
PCB Applications
Consumer Electronics
You use pcb technology every day, even if you do not notice. Your phone, laptop, and tablet need pcb design to work. These devices are small and strong because of advanced pcb features. Flexible and multilayer pcbs help fit more parts in thin gadgets. You also find pcb in things like microwaves, coffee makers, and fridges. TVs and video game consoles use pcb for fast signals and good performance.
Here are some common electronics that use pcb:
Smartphones and tablets
Laptops and desktop computers
Digital cameras and microphones
Video game consoles
Smart lights and home automation devices
Kitchen appliances like microwaves and fridges
Computer accessories such as mouse and keyboard
Printers and scanners
Without pcb, your devices would be big and weak. You would not have the cool gadgets you use every day.
Industrial and Automotive
Factories and cars need pcb for safety and automation. You see pcb in robots, PLCs, and smart sensors. These boards help machines move and make choices. Circuit board assembly in robots controls how they move. Machine vision systems use pcb cameras to check quality. AGVs in warehouses use pcb to find their way.
Car pcb must handle heat, shaking, and electrical noise. Engineers use special materials and coatings to protect the boards. Stiffeners and mounting methods stop damage from bumps. Circuit board assembly in cars controls the engine and entertainment.
Robots use pcb for movement and control.
AGVs use pcb to drive around.
Sensors check equipment health.
Motor drives and HMIs use pcb to talk to other parts.
Medical Devices
You trust medical devices to work safely. Pcbs in these tools must meet strict rules for quality and safety. Circuit board assembly in medical tools uses special materials like polyimide and ceramic. Flexible pcb fits into small or odd-shaped devices, like pacemakers and hearing aids.
Medical pcbs must follow rules like ISO 13485 and IEC 60601. These rules make sure the device works safely and lasts long. Testing checks for electrical safety, good performance, and strength.
Standard | Focus Area | Description |
|---|---|---|
ISO 13485 | Quality | Quality management for medical devices |
IEC 60601 | Safety | Electrical safety and performance |
IPC-A-600 | Acceptability | Circuit board condition standards |
FDA 21CFR820 | Regulatory | Manufacturing and quality system regulations |
Medical pcb must be strong and safe. People depend on them to stay healthy.
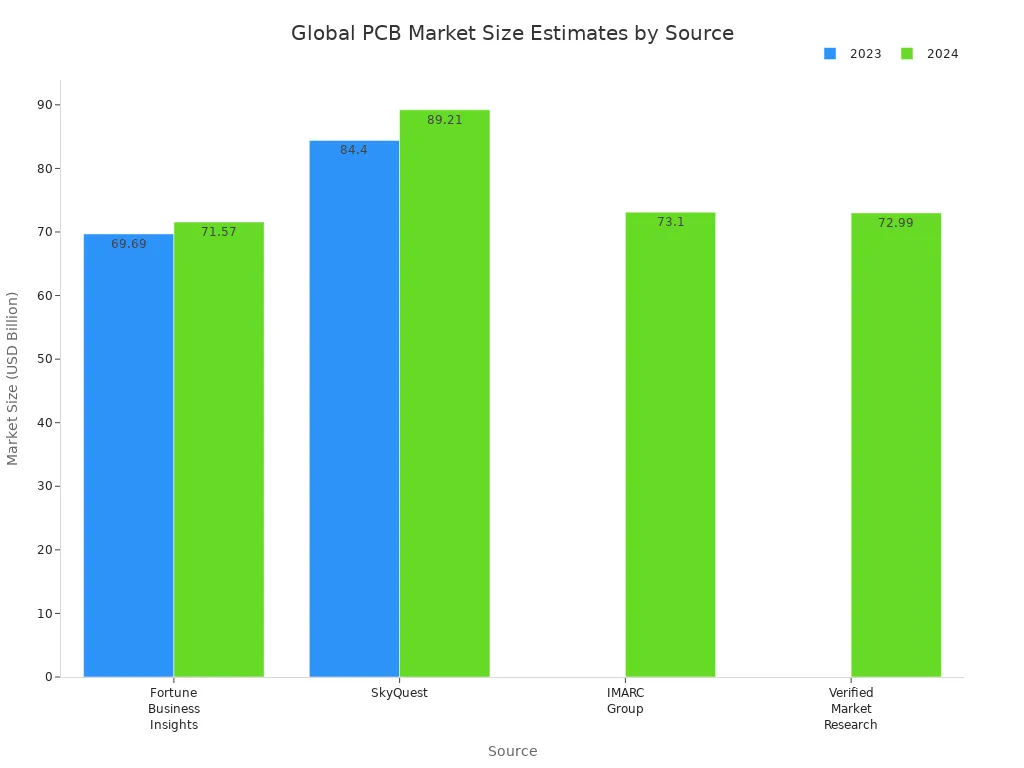
You can see that a pcb is very important in electronics. It holds all the parts and keeps them safe. A pcb lets your devices work the right way. The pcb market is getting bigger every year. This shows that pcbs are needed for new technology.
A pcb helps put devices together quickly and safely.
Knowing pcb basics makes it easier to learn electronics.
Try learning pcb design now so you can get better for the future.
FAQ
What does PCB stand for?
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. You see this term in electronics. It means the board that connects and supports electronic parts.
Why do you need a PCB in devices?
You need a PCB to organize and connect parts. It helps your device work safely and reliably. PCBs make devices smaller and easier to build.
Can you make a PCB at home?
You can make a simple PCB at home. You use copper boards, etching solution, and basic tools. Many beginners start with kits or online guides.
What materials do you find in a PCB?
You find fiberglass, epoxy resin, copper, and sometimes flexible plastics in a PCB. Each material helps the board stay strong and safe.
How do you identify a PCB in electronics?
You look for a flat board with copper lines and small parts. Most PCBs have a green or blue color. You see them inside phones, computers, and toys.
See Also
Understanding PCBA: Definition And Key Concepts In Electronics
The Importance Of PCB Design In Modern Electronic Devices
Exploring The Meaning And Function Of PCBA In Electronics
Defining PCBA And Its Essential Role Within Electronics
Breaking Down PCBA Abbreviation And Its Significance In Electronics