A printed circuit board, or PCB, is the foundation for electronic components. If you’re wondering, “whats a pcb,” it’s a board that holds and connects these components, making sure they work together. PCBs are found in nearly every modern electronic device. Many people ask, “whats a pcb?” because these boards are essential for supporting and linking electronic parts.
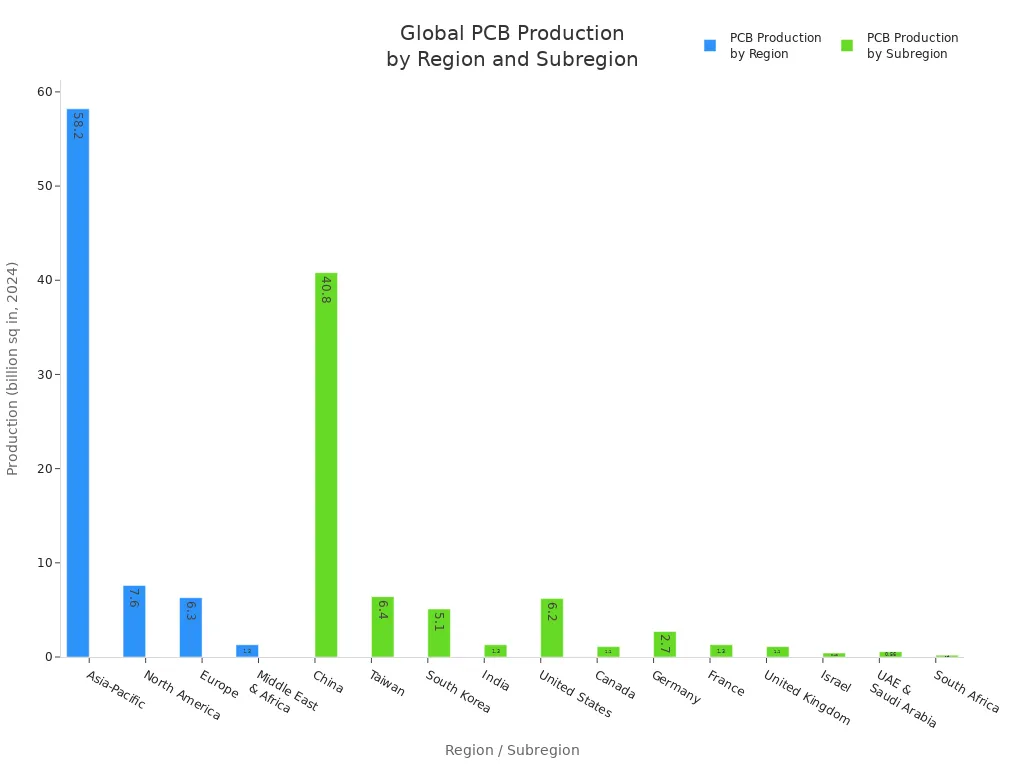
Manufacturers produce over 87 billion square inches of PCBs around the world every year.
Key Takeaways
A PCB is a board that keeps electronic parts in place. It connects these parts so devices can work safely. It also helps keep everything neat and tidy.
PCBs have copper lines that move electricity around. They come in many types and can have one or more layers. Some are for simple circuits, and some are for hard ones.
Learning about PCBs helps you build strong and small devices. It can also help you get jobs in electronics.
Whats a PCB
Basic Definition
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is the main base for electronic circuits. When someone asks, “whats a pcb,” it means a flat board made with layers that do not conduct electricity and thin copper sheets. The copper makes lines called traces. These traces connect parts of the circuit. Traces act like tiny roads. They carry signals between the parts.
Industry rules say a PCB is made of copper and layers that insulate. The copper is shaped into paths for electricity. The board can be stiff or bendy. This depends on what device uses it. Parts like resistors, capacitors, and transistors go on the board. Solder keeps these parts in place. It also connects them to copper pads. Multilayer PCBs use metal holes called vias. Vias link traces on different layers. This setup lets the board handle tough designs and fast electronics.
Note: PCBs give support and connect electricity, so they are needed for modern devices.
Role in Electronics
PCBs are important in every electronic device. They keep all the parts organized and connected. Without a circuit board, parts would need loose wires. That would be messy and not work well. The PCB design makes sure each part is in the right spot and connects the right way.
The main jobs of a PCB are:
Giving paths for signals and power.
Making assembly and fixing easy.
A circuit board has many types of parts. Each part does something special. The table below lists common parts and what they do:
PCB Component | Essential Function(s) |
|---|---|
Resistors | Control and limit current; adjust signals; set points for active parts |
Capacitors | Store and release energy; keep voltage steady; smooth power; filter noise |
Inductors | Store energy in a magnetic field; slow changes in current; filter signals |
Diodes | Let current go one way; protect from backward current; fix and control voltage |
Transistors | Make signals stronger; act as switches; control current; key in logic and digital circuits |
Integrated Circuits | Combine many parts to do hard jobs like signal work and saving data |
Connectors | Help connect the PCB to other devices or circuits |
Traces and Pads | Give paths for electricity and spots for parts; make sure things connect |
PCBs also use connectors, switches, and sockets. These link to other devices or let people control things. These features make the board strong and dependable. The PCB design helps stop mistakes, makes things work better, and helps make lots of devices.
PCBs are stronger than breadboards or point-to-point wiring. Breadboards are good for testing ideas. But they cannot handle lots of power or fast signals. PCBs let you build things that last and carry more current. They also help keep devices small and tidy.
Printed Circuit Board Structure
Materials and Layers
A printed circuit board is made from different materials. The most used one is FR-4. It is fiberglass cloth mixed with epoxy resin. This mix makes the board strong and safe for electricity. FR-4 can take high heat and does not bend easily. Some boards use polyimide to make them flexible. PTFE is used for boards that need to work at high frequencies. Metal core boards help move heat away from parts. Rogers laminates are picked for radio and microwave circuits because they have a low dielectric constant.
FR-4: Strong, stops fire, and not expensive
Polyimide: Bends and handles heat well
PTFE: Works in tough places and high frequencies
Metal core: Moves heat away from parts
Rogers laminates: Used in special communication devices
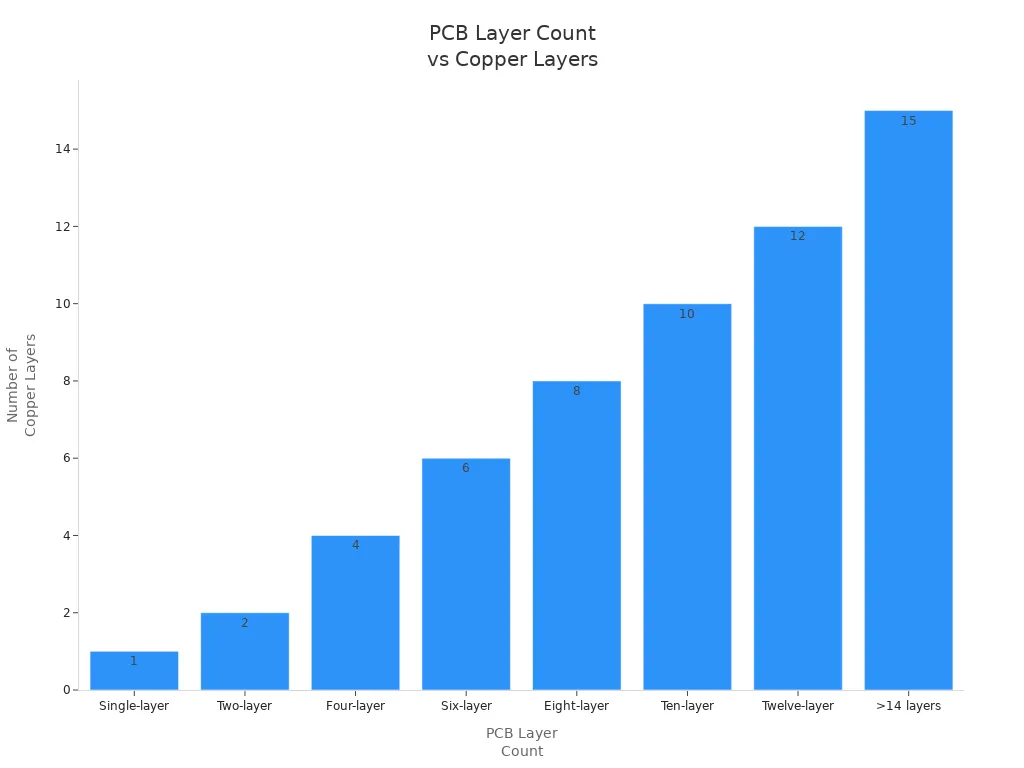
PCBs can have one or more layers. Each layer has a job, like carrying power or signals. The table below shows how many layers are common and what they do:
PCB Layer Count | Typical Layer Composition | Functions and Applications |
|---|---|---|
Single-layer | 1 copper layer + dielectric + soldermask | Used in simple things like calculators and LED lights |
Two-layer | 2 copper layers + dielectric + soldermask | Found in amplifiers and printers |
Four-layer | 4 copper layers + dielectric + soldermask | Used in handheld devices and medical tools |
Six-layer | 6 copper layers + dielectric + soldermask | Used in computers and big machines |
Eight-layer | 8 copper layers + dielectric + soldermask | Used in advanced computer systems |
Note: Picking the right materials and layers helps the pcb last longer and work better.
Conductive Pathways
Copper traces are the main paths on a pcb. These thin copper lines connect all the parts, like chips and resistors. The traces act like roads for electricity to travel. Copper is used because it is a good conductor and lasts long. The size of each trace depends on how much power it needs to carry. Thick traces carry more power. Thin traces fit in small spaces.
Copper traces connect every part on the board.
They take the place of messy wires and keep things neat.
Good pcb design uses the right trace size to stop overheating and signal loss.
The structure of a printed circuit board holds and connects all the parts. The layers that do not conduct, like fiberglass and epoxy resin, give the board its shape and strength. These layers keep the copper traces safe and in place. Together, the materials and traces help the circuit board work well in any device.
PCB Types and Uses
Main Types
PCBs have different types for different jobs. The most common types are single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs. Each type works best for certain electronics. The table below shows how they are different:
Feature | Single-Sided PCB | Double-Sided PCB | Multi-Layer PCB |
|---|---|---|---|
Number of Conductive Layers | 1 | 2 | 3 or more |
Circuit Complexity | Simple | Moderate | High |
Cost | Low | Moderate | High |
Durability | Low | Moderate | High |
Applications | Basic circuits, simple devices | Complex circuits, wearables, automotive | High-performance applications like smartphones, medical devices, automotive |
Manufacturing Time | Short | Moderate | Long |
Single-sided PCBs have copper on one side. They are used in simple things like calculators and cameras. Double-sided PCBs have copper on both sides. Vias help connect the two layers. These boards can hold more parts and harder circuits. You find them in car dashboards and phone systems. Multi-layer PCBs have three or more copper layers. They are used for computers, smartphones, and medical tools.
Applications
PCBs are inside many things people use every day. In electronics, PCBs are found in smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smartwatches. TVs, video game consoles, and stereos also need PCBs. Home items like fridges, microwaves, and coffee makers use PCBs to work.
Cars use PCBs for safety, maps, and music. Driver help and electric cars need strong boards that can handle heat and shaking. Medical tools need PCBs for pacemakers, tests, and pictures. Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs fit into tight spaces and tough places.
PCB making keeps growing as new tech comes out. Engineers use better stuff and new ideas to make boards last longer and work faster. PCB design helps keep devices small and working well. As tech gets better, PCBs become even more important in our lives.
A pcb holds and links electronic parts. This helps devices work well and safely. Learning about pcb design teaches you to solve problems. It also helps you think in creative ways. You can make circuits that last a long time. These circuits also work better.
Engineers and hobbyists use pcb skills to make small, strong devices.
PCBs help electronics stay small, tough, and simple to repair.
Learning about pcb technology can lead to new ideas. It can also help you find jobs in electronics.
FAQ
What does PCB stand for?
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It supports and connects electronic components in devices.
Why do engineers use copper in PCBs?
Copper conducts electricity well. It creates strong, reliable paths for signals and power on the board.
Can a PCB be flexible?
Some PCBs use flexible materials. These boards bend and fit into small or oddly shaped spaces.
See Also
Understanding PCB Design And Its Importance In Electronics
Exploring The Meaning Of PCBA And Its Electronics Role
Defining PCBA And How It Functions In Electronics