Showing 1–12 of 56 results
-
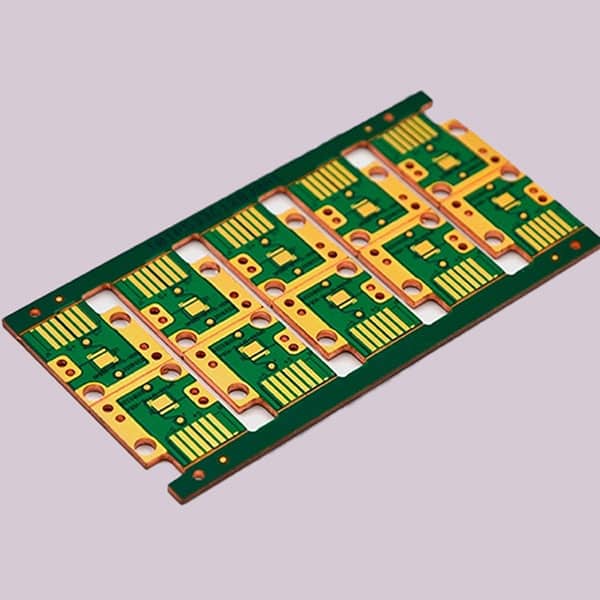
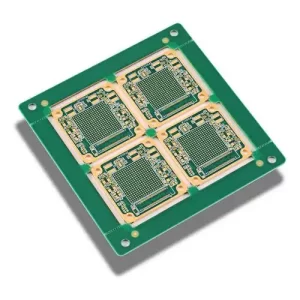
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
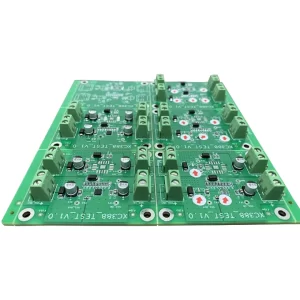
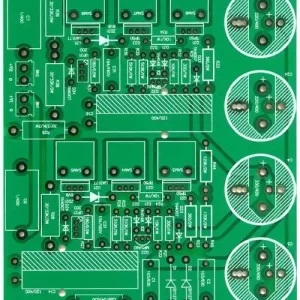
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
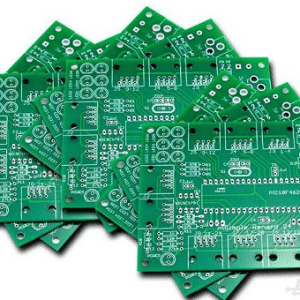
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
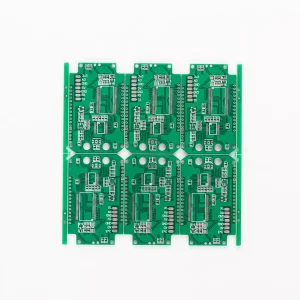
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Dual panel
Dual panel
A Double-Layer PCB (Double-Sided PCB) is a type of printed circuit board that has copper traces on both sides of the board. Unlike Single-Sided PCBs, these boards allow for more complex circuits by using vias (plated-through holes) to connect the layers electrically.
-
Flexible plate
Flexible plate
A Flexible PCB (FPC), also known as a Flex Circuit, is a type of printed circuit board that is designed to be bent, twisted, or folded without breaking. Unlike rigid PCBs, FPCs use flexible materials like polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) instead of traditional FR4.
-
Flexible plate
Flexible plate
A Flexible PCB (FPC), also known as a Flex Circuit, is a type of printed circuit board that is designed to be bent, twisted, or folded without breaking. Unlike rigid PCBs, FPCs use flexible materials like polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET) instead of traditional FR4.