In 2025, understanding what pcb means is key to knowing the main difference between pcb and pcba in electronic devices. PCB means a plain circuit board that provides support and allows electricity to flow. PCBA, on the other hand, is what you get after adding components like chips and resistors to the board, making it a working unit. This difference is important for engineers, buyers, and manufacturers. The pcb means the base board, while the pcba is the completed, usable board.
The global circuit board market continues to expand, driven by the demand for advanced devices and new technology.
PCB and PCBA market size was $67.65 billion in 2024 and could reach $85.88 billion by 2032.
The Asia-Pacific region produces the most boards, with China as a leading manufacturer.
Market growth is fueled by the automotive, consumer electronics, and healthcare electronics sectors.
Key Takeaways
A PCB is just a plain board that holds and links parts. A PCBA is a PCB with all the parts put on it, so it works as a device.
PCBs cost less and are good for tests or easy projects. PCBAs cost more because they have parts and need assembly, but they are ready to use in products.
Making a PCB takes time, depending on how hard it is. Making a PCBA takes more time because you must add and check parts. So, it is important to plan for both steps.
PCBs and PCBAs are used in many electronics like phones, cars, medical tools, and 5G gear. New trends want boards to be smaller, smarter, and better for the planet.
Picking the right materials and suppliers is important. Knowing the cost and time helps make good boards and smooth production in 2025.
PCB Means and Types
PCB Definition
In 2025, pcb means a printed circuit board. It is the base for almost all electronics. The board holds and connects important parts like resistors and chips. Copper lines on the board let electricity move between these parts. The board gives support and lets power flow. This makes it very important in today’s electronics.
PCB Types in 2025
Manufacturers make many types of printed circuit boards. These boards fit the needs of different industries. By 2025, High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs are the most used in new devices. These boards help make gadgets smaller and stronger. Flexible and rigid-flex PCBs are also common. They can bend and fit into special shapes. This is useful for wearables and medical tools.
PCB Type | Key Characteristics | Advantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
Single-Sided | One layer with metal on one side | Cheap, easy to make | Simple gadgets, calculators, LED lights |
Double-Sided | Metal layers on both sides | More circuits, not too hard to make | Car dashboards, power supplies |
Multilayer | Three or more metal layers with insulation | Small, good for hard circuits | Phones, computers, medical tools |
Rigid | Hard, does not bend (often FR-4) | Strong, saves money | Home gadgets, factory machines |
Flexible (Flex) | Bends easily | Saves space, light | Wearables, medical tools, car wires |
Rigid-Flex | Mix of hard and bendy parts | Strong and bends | Planes, medical implants, foldable gadgets |
Metal-Core (MCPCB) | Metal base for better cooling | Great at moving heat away | LED lights, car headlights |
Ceramic | Ceramic base, handles heat well | Handles heat, resists chemicals | Radio circuits, space gadgets |
HDI | Uses tiny holes and new tech | Fits lots of parts, better signals | Phones, tablets, wearables |
High-Frequency | Special base for radio waves | Keeps signals clear, less loss | 5G, radar, satellites |
PCB Materials
PCB makers in 2025 use many materials for different needs. FR-4 is a strong fiberglass and is used for hard boards. Polyimide is used for bendy boards because it does not break. Rogers and PTFE are picked for high-frequency boards. Metal-core and ceramic bases help cool down hot boards. Each material helps the board stay strong and safe.
Tip: Picking the right board material changes how well it works, how much it costs, and if it lasts in tough places.
PCB Uses
Printed circuit boards are used in many fields. Computers, phones, and TVs need fast and smart boards. Cars and hospitals use multi-layer and rigid-flex boards for safety. Data centers, AI, planes, and the military also need special boards. The pcb means more than just a base; it is the heart of modern tech.
PCBA Overview
PCBA Definition
PCBA means printed circuit board assembly. It is a PCB after adding all needed parts. A bare PCB cannot do anything by itself. A PCBA can do special jobs in electronics. To make a PCBA, workers put on and attach parts like resistors, capacitors, and chips. This changes the board from just a base into a working device.
Aspect | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
Definition | Bare board with no parts, lets electricity flow | Board with all parts added, works as a full circuit |
Function | Holds parts and lets power move | Does a certain job in electronics |
Components | No parts on it | Has all needed parts like resistors and chips |
Manufacturing | Makes copper lines and covers the board | Adds and attaches parts to the board |
Testing | Checks for breaks or shorts in copper lines | Checks if the board works right with all parts |
Stage | Start or base of the device | Finished and ready to use |
Applications | Used to test ideas and build first models | Used in things like phones, computers, and machines |
PCBA Process
The pcb assembly process in 2025 has many steps. First, engineers draw the board using computer programs. Then, factories make the plain PCB. Next, they put solder paste on the board. Machines place each part in the right spot. The board goes through heat to stick the parts on. Workers check the board by looking, using cameras, and X-rays. At the end, they test if the board works as it should. These steps help make sure every PCBA is high quality.
PCBA Role
PCBA is very important in today’s electronics. It links chips, memory, sensors, and other parts. This helps devices work well and fast. New machines and robots make building PCBAs quicker and more exact. New materials help the boards handle heat and send signals better. PCBA lets gadgets get smaller and do more things, like in phones and smart watches. In medicine, PCBA helps fake arms and legs move when people want. Careful checks make sure each PCBA works well, even in hard jobs.
PCB vs PCBA
Core Differences Between PCB and PCBA
When you look at pcb vs pcba, you see big differences. They are not the same in what they are made of or what they do. A pcb is just a plain board. It is made from things like fiberglass or epoxy. The board has copper lines, a solder mask, and silkscreen. Sometimes it has holes called vias. This board is the base for all electronics.
A pcba is the next step after the pcb. It has all the parts put on the board. These parts can be resistors, capacitors, transistors, and chips. Workers use special ways to put parts on the board. Surface Mount Technology puts parts on top. Through-Hole Technology puts part leads through holes and solders them.
PCB:
Gives support and paths for electricity.
Used to test and try new ideas.
PCBA:
PCB with all parts added and soldered.
Works as a full, working circuit.
Used in finished products and big batches.
The main difference is in how far along they are made. The pcb is just the start. The pcba is the part that makes things work.
Similarities
Even though they are different, pcb and pcba are also alike. Both start with the same kind of board. The pcb is the base for both. Each board has layers like the substrate, copper, solder mask, and silkscreen. These layers help connect parts and keep things cool.
Both pcb and pcba help connect electronic parts. The pcb helps with the layout and design. The pcba makes the board work by adding parts. In every device, the board is very important.
Note: Every pcb and pcba starts with a printed circuit board. This makes it a must-have for all electronics.
PCB vs PCBA Cost
The price difference between pcb and pcba comes from what goes into them. A pcb is cheaper because it is just the board. It only has the base, copper, solder mask, and silkscreen. Making it means drawing, cutting, drilling, and finishing the board.
A pcba costs more because it has extra parts and work. Machines put and solder the parts on the board. There are more steps like checking and testing to make sure it works. The price of a pcba depends on how many parts, how hard it is to make, and how much checking is needed.
PCB: Cheaper, good for testing and first ideas.
PCBA: Costs more, includes parts, work, and testing.
The cost shows the main difference between pcb and pcba. The pcb is just the start. The pcba is ready to use and works right away.
PCB vs PCBA Time
Time is also important when looking at pcb vs pcba. How long it takes to make a pcb depends on how hard and how many you need. Easy boards can take 1–2 weeks. Hard or big orders can take up to 8 weeks. The steps are design, making, and checking.
PCBA can be faster for simple boards. Small batches can be done in 1–5 days. Big or hard jobs can take 10–20 days or more. The total time for pcba is the time to make the board plus the time to add parts.
Process Stage | Lead Time Range (Business Days) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
PCB Fabrication | Time depends on how hard the board is | |
PCB Assembly (Prototype) | 1–5 days | Time for small test runs |
PCB Assembly (Low Volume) | 5–10 days | Time for small batches |
PCB Assembly (Medium to High Volume) | 10–20+ days | More time for bigger or harder jobs |
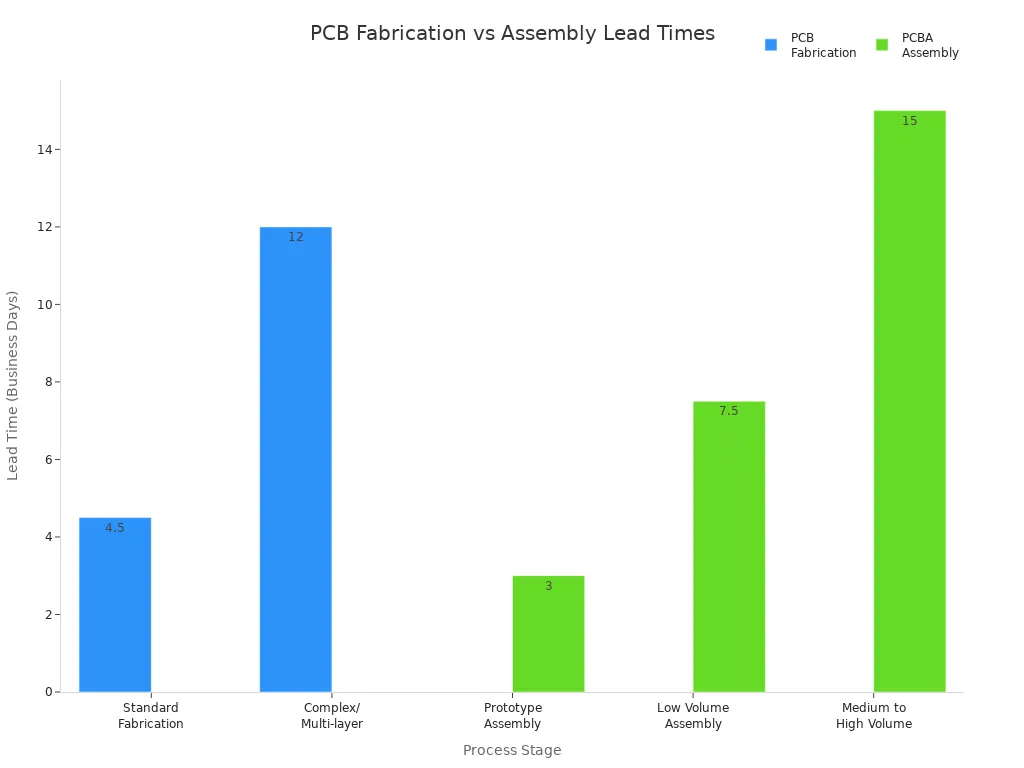
The total time for a pcba is both making the board and adding parts. For small jobs, making the board can take as long as adding parts. For big or hard jobs, adding parts can take even longer.
Tip: Plan for both pcb and pcba times. This helps you finish your product on time and keeps things running smoothly.
Applications in 2025
PCB Applications
In 2025, pcb technology is used in many areas. Engineers make small and powerful boards for new electronics. These boards help make gadgets smaller and smarter. Flexible and rigid-flex pcb designs are found in foldable phones and wearables. They are also used in new medical tools. High-frequency printed circuit boards are important for wireless things like 5G, GPS, and radar. Many companies use special materials like ceramics and Teflon. These help boards handle heat and keep signals clear.
Smartphones, tablets, and computers
Wearable health monitors and smartwatches
Car sensors and engine controls
Machines for factories
Airplane communication and monitoring systems
LED lights for homes and hospitals
Note: Many companies now care about the environment. They use lead-free soldering and materials that can be recycled.
PCBA Applications
PCBA helps new ideas in many fast-growing fields. Consumer electronics use the most, with over 40% of the market. Companies make new phones, smart home gadgets, and wearables. Cars use more pcba, especially electric cars and smart driving systems. More 5G networks mean more need for strong pcb assembly in base stations and routers. Medical electronics need careful assembly for things like infusion pumps and pacemakers. IoT devices in homes, factories, and hospitals need small and dependable printed circuit board assembly.
Main areas using pcba:
Consumer electronics
Cars and electric vehicles
5G network equipment
Medical and wearable health devices
Factory IoT and automation
Industry Trends
In 2025, the industry follows some big trends. Automation and AI make pcb assembly faster and more exact. Smaller devices can do more things now. Companies use green ways to make boards, like eco-friendly materials. Flexible and rigid-flex pcb types help with new designs in wearables and cars. More IoT means more need for custom, low-power boards with sensors. Makers build smart factories and use real-time checks to stay ahead.
Tip: Knowing the latest trends helps companies make better products and keep up with what customers want.
Manufacturing and Supply Chain
Manufacturing Steps
Making PCB and PCBA in 2025 uses careful steps. Factories use smart machines to make things faster and more exact. The usual steps for making a PCB are:
Pick the right materials for the board.
Make the inside layers and add images.
Etch the inside layers and check them.
Treat with brown oxide so layers stick better.
Stack and press the layers together.
Drill holes for parts to connect.
Clean and smooth the holes.
Put thin film on the outside layers.
Plate copper in the holes.
Add images and plate copper on the outside.
Etch and check the outside layers.
Use X-rays to check if layers line up.
Put on solder mask and add images.
Print labels with silkscreen.
Cut the board shape with a CNC machine.
Test with flying probes for electricity.
Do a final quality check.
Test again with machines to be sure.
Pack boards in vacuum bags to keep them safe.
PCBA adds more steps like putting on parts, soldering, and testing many times. Factories use both machines and people to test each board. This makes sure every board is good and works well.
Cost Factors
How much it costs to make a board depends on many things. The materials, how hard the board is, and how many layers it has all change the price. Boards that work at high frequencies or have lots of layers cost more. Using robots and smart machines helps save money on workers and lowers mistakes. Testing and checking the boards costs more but stops bad boards from being sent out. Making lots of boards at once makes each one cheaper. Companies also save by reusing copper and picking better materials.
Cost Driver | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|
Material selection | High for advanced PCB |
Board complexity | Increases with layers |
Automation | Lowers labor cost |
Testing | Adds to total cost |
Batch size | Larger runs save cost |
Tip: Spending more on good testing and smart machines can save money later by stopping problems.
Supply Chain in 2025
In 2025, the supply chain for PCB and PCBA uses AI, robots, and smart factories. These tools help make boards faster and better. Companies care about the planet and use lead-free solder and green materials. New factories in Asia, Latin America, and Africa make boards faster and cheaper. But there are still problems. Not enough raw materials, late shipping, and bad quality can slow things down. To fix this, companies use more than one supplier, keep extra materials, and recycle. They also test and check boards at every step. Good shipping partners and local warehouses help stop delays. Training workers and updating machines keeps everything running well.
Note: A strong supply chain with smart tools and good planning helps companies send out good products on time.
Summary Table
A simple table helps people pick the right option. It lets engineers, buyers, and makers compare PCB and PCBA easily. The table below shows the main ways they are different in 2025. It talks about cost, how long they take to make, and how they fit into new electronics.
Aspect | PCB (Printed Circuit Board) | PCBA (PCB Assembly) |
|---|---|---|
Cost | The price changes with how hard the board is, its size, layers, and what it’s made of. Easy boards cost $5–$20 each. Medium ones cost $20–$30. Hard or small orders can be $30 or more. Each square inch costs $0.50 to $5. | PCBA costs more because it adds labor, machines, and parts. The price goes up with assembly. Buying many at once makes each one cheaper. Hard builds follow the same price steps. |
Time | How long it takes depends on the board’s design and how many you need. Normal schedules are cheaper. Faster jobs cost more. | Assembly time adds to the total time. Fast assembly means you get it sooner but pay more. Both steps need good planning. |
Application | PCB is the base for all electronics. What it’s made of and how many layers it has depends on what it will be used for, like phones, cars, or radio devices. | PCBA is ready to use in products. It is best for hard devices that need lots of parts and must work well. |
Note: What you pick for materials changes how well it works and how much it costs. DIY boards are fine for easy projects, but experts say to let pros handle hard designs.
A table like this gives a fast look at the facts. It shows how each step, from plain board to finished build, changes cost, time, and use. People can use this to plan, save money, and finish on time.
PCB and PCBA do not do the same job in electronics. PCB is just the plain board with no parts on it. PCBA is the board with all the parts added, so it can work. They both start with the same base, but they are not the same in price, time, or how hard they are to make. Engineers and buyers should think about what their project needs. This means looking at how many layers the board has, what it is made of, and how it will be tested. They should pick suppliers who have good quality checks and the right certificates. It is smart to think about cost, how fast you need it, and if the supply chain is steady to get the best outcome.
FAQ
What is the main difference between PCB and PCBA?
A PCB is just a board with copper lines. A PCBA has all the parts put on it. The PCBA can do jobs in a device, but the PCB cannot.
Can a PCB be used without assembly?
No, a PCB by itself cannot work in anything. It needs parts like chips and resistors. It only works after all the parts are added.
How do engineers choose between PCB and PCBA for a project?
Engineers use a PCB to test ideas or try layouts. They pick a PCBA when they need a working circuit for a product.
What factors affect the cost of PCB and PCBA?
The type of material, how hard the board is, and how many you make change PCB cost.
PCBA cost also has labor, part prices, and testing.
Are PCBs and PCBAs recyclable?
Yes, many companies recycle both PCBs and PCBAs. They get metals back and use materials again. Green ways help cut down waste in 2025.
See Also
Understanding The Main Distinctions Between PCB And PCBA
Uncovering The Lesser Known Variations Between PCBA And PCB
Analyzing Functional And Structural Contrasts Of PCBA Versus PCB