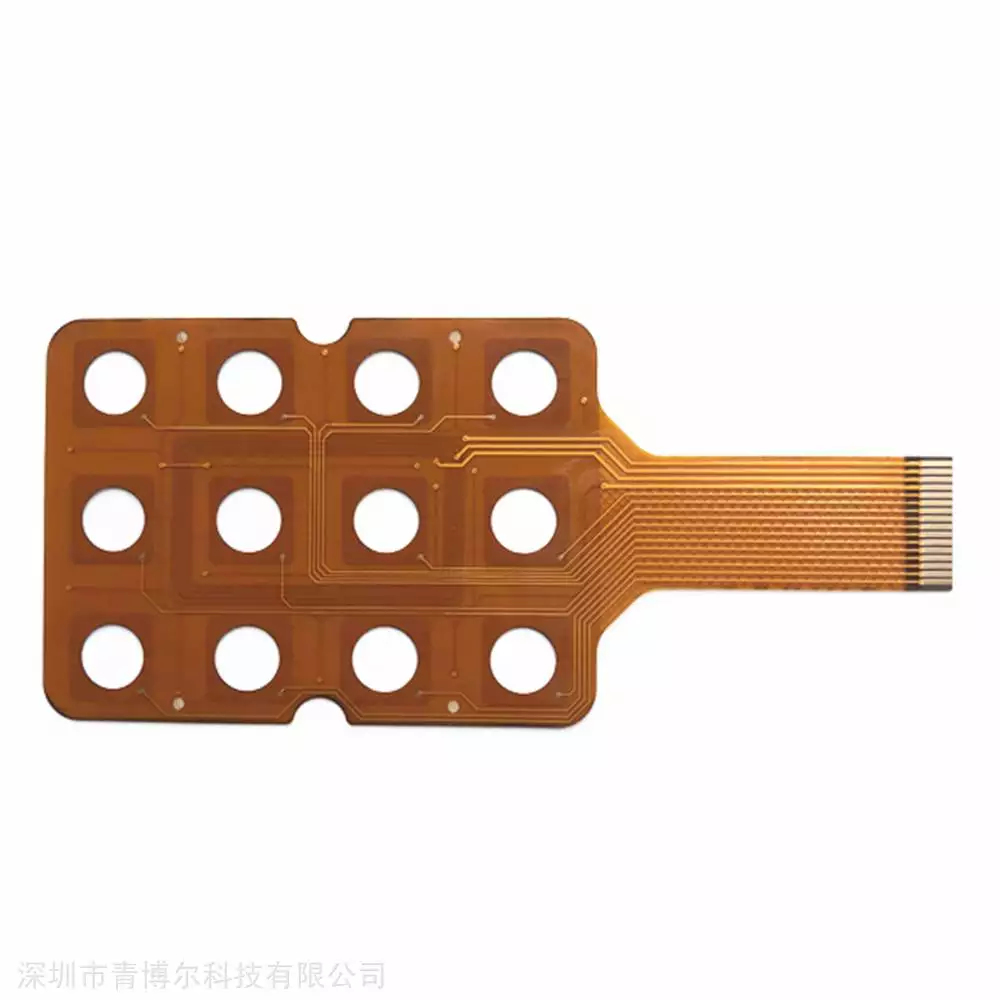
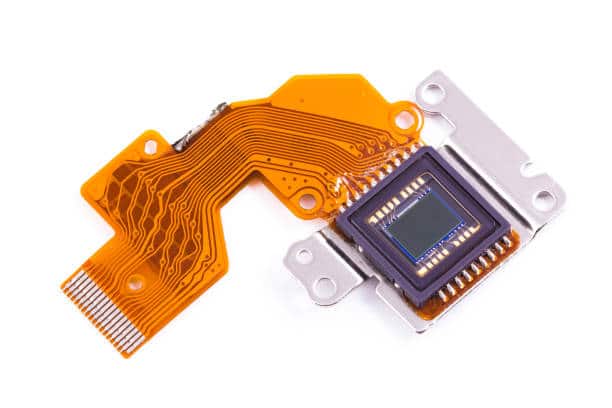
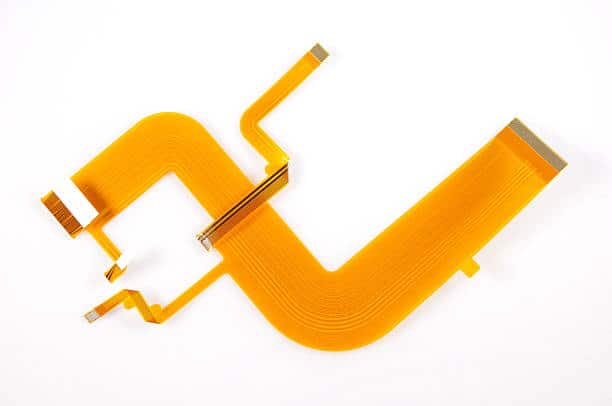
Common Applications of Flexible PCBs(FPC):
✅Consumer Electronics – Smartphones, wearables, foldable displays.
✅Medical Devices – Pacemakers, hearing aids, diagnostic equipment.
✅Automotive Electronics – Airbag sensors, dashboard circuits, LED lighting.
✅Aerospace & Defense – Satellite systems, avionics, and military equipment.
✅Industrial Equipment – Robotics, automation, and flexible sensors.
Advantages of Flexible PCBs (FPCs)
|
Lightweight & Thin
|
FPCs are significantly thinner and lighter than rigid PCBs, making them ideal for compact and lightweight electronic devices.
|
|
Flexible & Bendable
|
Can be bent, twisted, or folded without breaking, allowing for unique and space-saving designs.
|
|
Space-Saving & High-Density
|
Supports high-density circuit designs in limited spaces, reducing the need for bulky wiring and connectors.
|
|
Durability & Reliability
|
Withstands vibration, shock, and movement better than rigid PCBs, reducing mechanical failures.
|
|
Fewer Interconnections Needed
|
Eliminates the need for connectors, solder joints, and cables, reducing points of failure.
|
|
Better Heat Dissipation
|
The thin, flexible material allows heat to dissipate more efficiently, enhancing performance.
|
|
Increased Design Freedom
|
Enables 3D circuit designs, allowing integration into curved or irregular shapes.
|
|
Improved Signal Integrity
|
Shorter signal paths reduce electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
|
|
Cost Reduction in Assembly
|
Reduces wiring complexity, assembly time, and material costs in mass production.
|
Flexible PCB (FPC) Manufacturing Process
The Flexible PCB (FPC) manufacturing process involves multiple steps to ensure high reliability, flexibility, and performance. Below is a detailed step-by-step process:
1.Design & Gerber File Preparation
Circuit design is created using PCB CAD software (e.g., Altium, Eagle, KiCad).
The design includes flexible substrate considerations, bend areas, and component placements.
Gerber files are generated and sent to fabrication.
2.Material Selection & Preparation
Flexible Substrate: Typically Polyimide (PI) or Polyester (PET) for flexibility and heat resistance.
Copper Foil: Used for conductive traces.
Adhesive or Adhesiveless Lamination: Depending on the FPC type.
3.Copper Patterning (Etching Process)
Photoresist Application: A UV-sensitive film is applied to the copper-clad substrate.
UV Exposure & Development: The circuit pattern is transferred using UV light and a mask.
Etching: Unprotected copper is removed using a chemical solution (e.g., ferric chloride) to form the circuit traces.
Photoresist Stripping: The remaining protective layer is removed.
4.Drilling (Via & Component Holes)
CNC Drilling: Used to create holes for components and electrical connections (vias).
Laser Drilling: Used for micro-vias in HDI flexible circuits.
5.Plated Through-Hole (PTH) Process (For Multilayer FPCs)
Holes are plated with copper electroplating to ensure electrical connectivity between layers.
6.Coverlay Application (Protective Layer)
Coverlay Film (Polyimide) is applied over the copper traces to protect from oxidation, solder bridging, and mechanical damage.
The coverlay is laminated and laser-cut to expose solder pads.
7.Surface Finishing (Improves Solderability & Durability)
Common surface finishes:
ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) – High reliability.
OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative) – Lead-free and cost-effective.
HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) – Common but less flexible.
8.Silkscreen Printing (Optional)
Component labels, logos, and markings are printed using screen or inkjet printing.
9.Circuit Testing & Inspection
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI): Detects etching and alignment errors.
Electrical Testing (Flying Probe or Bed-of-Nails): Ensures continuity and circuit integrity.
10.Profiling & Cutting
FPCs are laser-cut or punched into their final shape based on design specifications.
11.Final Cleaning, Packaging & Delivery
The PCBs are cleaned to remove contaminants.
Inspected, packed, and shipped for assembly (PCBA) or direct use.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.